| Aspera Sync |
257
Using the Aspera Watch Service with Aspera Sync
Aspera Sync can use asperawatchd for more efficient file system change detection, particularly for file systems with
many files.
Starting Aspera Watch Services and Creating Watches
The Aspera Watch Service (
asperawatchd
) is a file system change detection and snapshot service that is
optimized for speed, scale, and distributed sources. On file systems that have file system notifications, changes in
source file systems (new files and directories, deleted items, and renames) are detected immediately, eliminating
the need to scan the file system. On file systems without file notifications, such as object storage, Solaris, AIX, and
Isilon, file system scans are automatically triggered.
The Aspera Watch Service can be used on any local or shared (CIFS, NFS) host. However, when watching mounted
shared storage and the change originates from a remote server, the Watch Service does not receive file notifications.
In such cases, set
<scan_period>
in
aspera.conf
to frequent scans, such as 1 minute. See the following steps
for instructions.
When used in conjunction with
ascp
commands, the Aspera Watch Service enables fast detection and transfer of
new and deleted items. For more information on using watches with
ascp
, see
Transferring and Deleting Files with
on page 216.
To start the Aspera Watch Service and subscribe to (create) a watch:
1.
Configure a docroot or restriction for the user.
Docroots and path restrictions limit the area of a file system or object storage to which the user has access. Users
can create Watch Folders and Watch services on files or objects only within their docroot or restriction.
Note:
Users can have a docroot or restriction, but not both or Watch Folder creation fails.
To set up a docroot from the command line, run the following command:
# asconfigurator -x "set_user_data;user_name,
username
;absolute,
docroot
"
Restrictions must be set from the command line:
# asconfigurator -x
"set_user_data;user_name,
username
;file_restriction,|
path
"
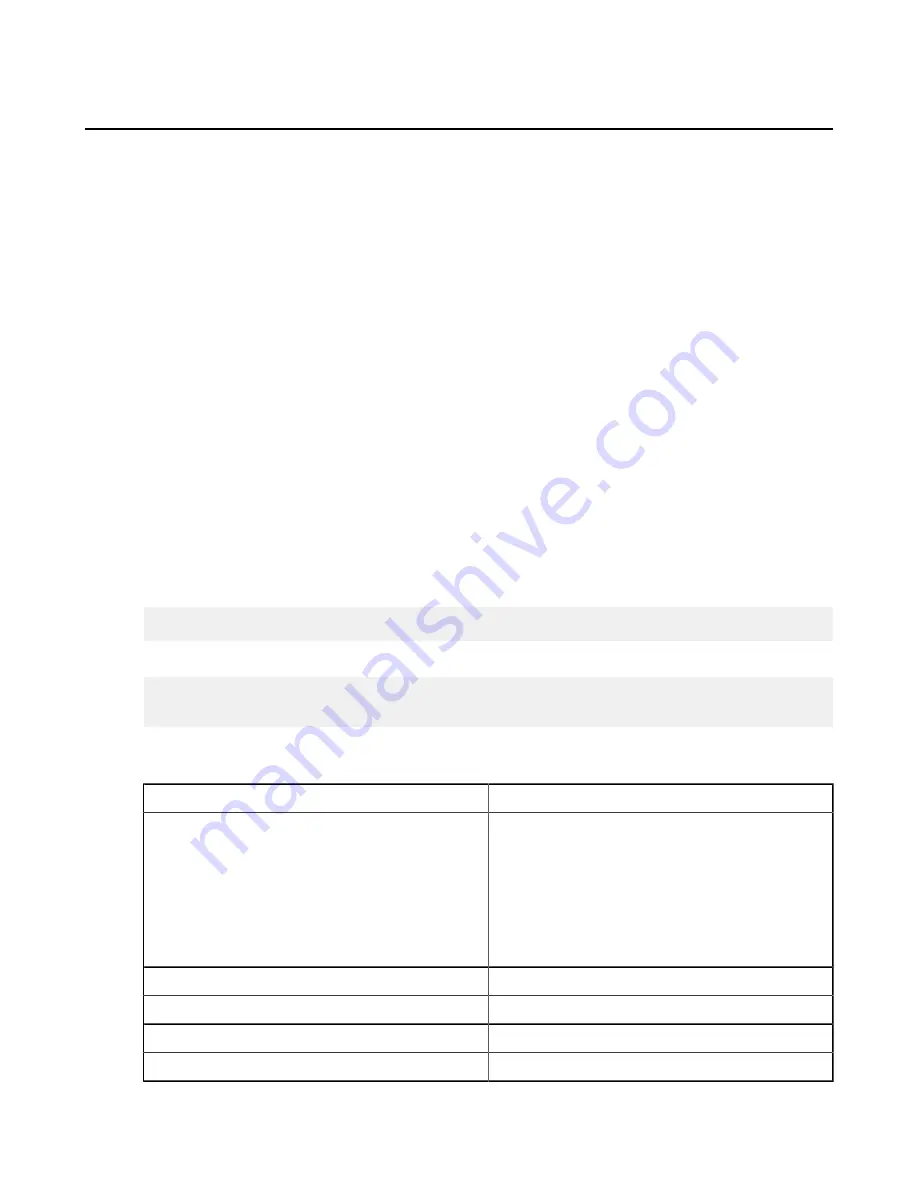
The restriction path format depends on the type of storage. In the following examples, the restriction allows access
to the entire storage; specify a bucket or path to limit access.
Storage Type
Format Example
local storage
For Unix-like OS:
• specific folder:
file:////
folder
/*
• drive root:
file:////*
For Windows OS:
• specific folder:
file:///c%3A/
folder
/*
• drive root:
file:///c*
Amazon S3 and IBM Cloud Object Storage - S3
s3://*
Azure
azu://*
Azure Files
azure-files://*
Azure Data Lake Storage
adl://*