4 Quick-start guide
4.4.9
Angle encoder identification (automatic
determination)
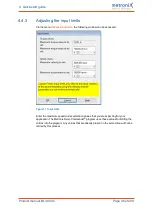
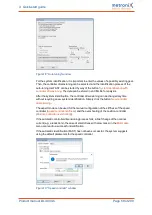
The angle encoder is automatically identified during the commissioning process. The
following parameters are determined during the identification:
l
Number of pairs of poles
l
Angle encoder offset
l
Phase sequence of the angle encoder (anti-clockwise, clockwise)
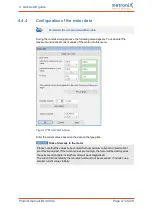
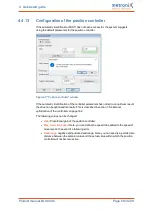
Outside of the commissioning process, the function can be accessed via the following
menus:
l
Parameters/Device parameters/Motor data
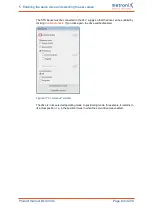
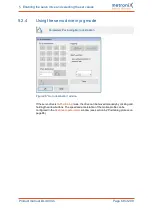
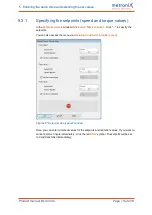
: button
Auto detect
l
Parameters/Device parameters/Angle encoder settings
: button
Auto detect
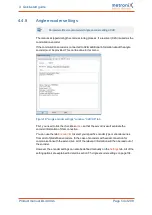
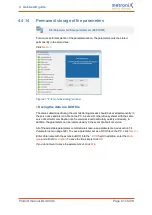
The following conditions must be fulfilled for an automatic identification:
l
The motor is completely wired and connected to earth
l
The DC bus voltage is present
l
The servo drive is free from errors
l
The STO inputs are connected to the 24 V supply
l
The shaft can move freely
Damage to property caused by incorrect data
Incorrect angle encoder data may lead to uncontrolled movements of the drive. This
may cause damage to the motor or to the entire system.
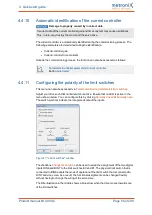
A failure of the automatic identification may be due to the following:
l
The parameterised motor current is too low or the motor shaft cannot move
l
If there are several servo drives in the same control cabinet, another encoder than
the one belonging to the motor is connected to the servo drive
l
Incorrect encoder configuration
l
Defective motor (this must be analysed by measuring the winding resistance
values)
l
Not all of the phases are connected. This must be analysed by measuring the
winding resistance values at the motor connector of the servo drive
Product manual BL 4000-C
Page 55 of 298