6 Applications
6.3
Applications with several angle encoders
So far, only applications with a single angle encoder have been discussed. The angle
encoder provides information about the commutation position and about the actual speed
and position. The individual pieces of information can also be provided by more than one
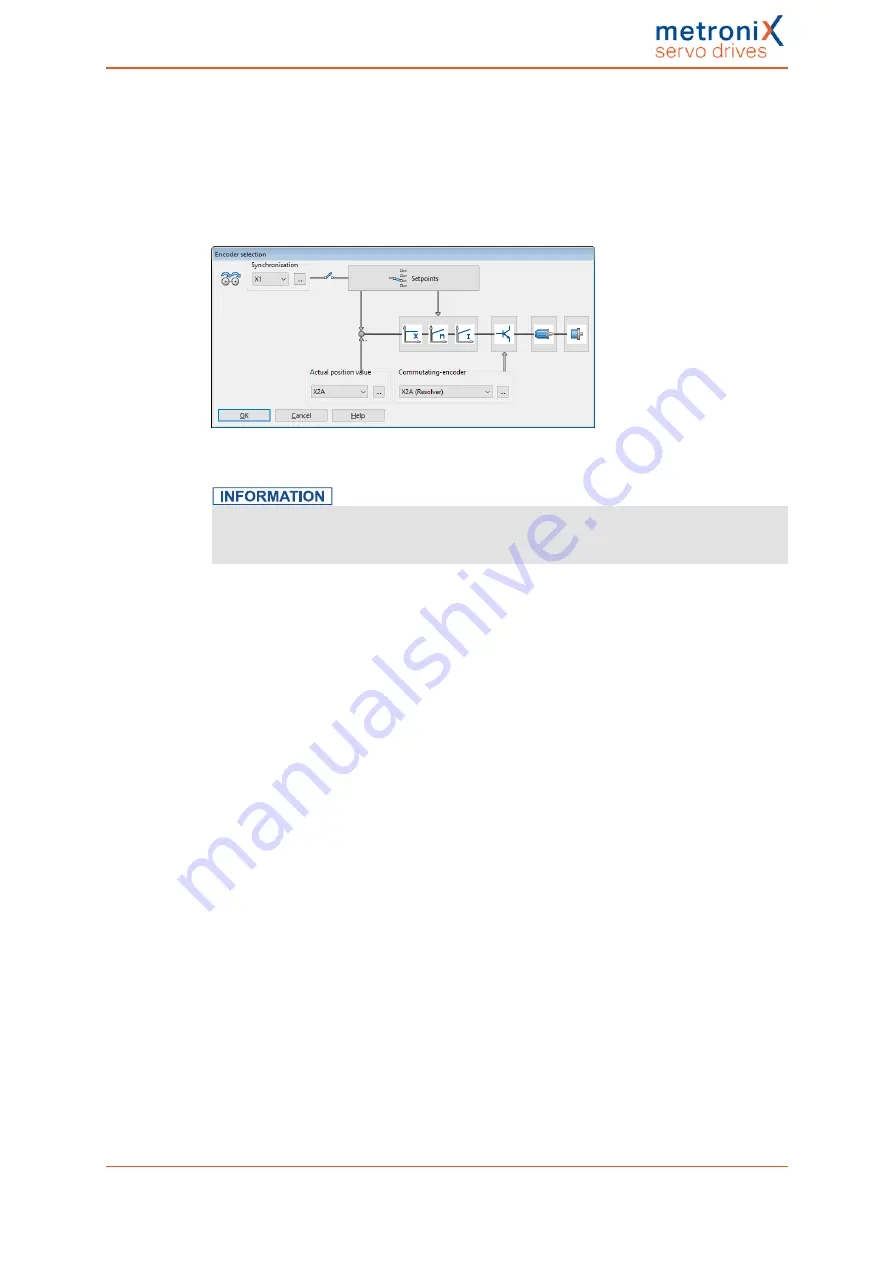
encoder. To do so, open the menu
Operating mode/Encoder selection
.
Figure 59: "Encoder selection" window
Commutation position and actual speed value
The information about the commutation position and actual speed value is always
provided by the same angle encoder!
Using a separate angle encoder for the position information may be useful in the following
case:
The motor is connected to a positioning mechanism via a transmission. The positioning
mechanism must fulfil extremely high requirements in terms of its accuracy. The
positioning mechanism has a high-resolution angle encoder. In this case, it makes sense
to use this information for the determination of the current position, while the speed and
commutation position information is still provided by the motor encoder.
Another class of applications can be summarised under the concept of "synchronisation".
In this case, several servo drives are synchronised by coupling them in a master-slave
setup. The master provides the slave with the position information via the master
frequency output (X1) and the slave receives this information via the external master
frequency input (X1). For this setup, the connectors must be connected by way of a cable.
The master operates in one of the operating modes described earlier (
speed control
,
positioning mode
), while the slave operates in synchronised mode.
Among others, the following applications are possible with this configuration:
l
Speed-synchronous movement
l
Position-synchronous movement
l
Flying saw
Product manual BL 4000-C
Page 104 of 298
















































