Chapter 8. Communication Function
8-77
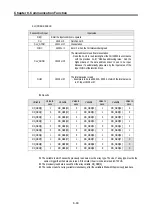
Ex1) CD 01
Function block input
Input value
REQ
Enter the input condition to operate
CH
16#0 or 0
Set channel (0, 1)
SLV_ADDR
16#11 or 17
Slave station
FUNC
16#0F or 15
Enter ‘15’ as bits are continually written on the output coils.
ADDR
16#13 or 19
Set the starting address to write on the slave station
-
Write on no. 19, starting from Holding Register 00020 in
accordance with the previous no. 8) “Modbus addressing rules.”
The highest data of the data address doesn’t need to be input.,
because it’s automatically processed by the input value in the
input FUNC of the function block.
NUM
16#0A or 10
Set the number of data to write on the slave station..
-
Example is to be read from 00020, of which the total data size is
10. Input 16#0A.
z
Result
From the 2 bytes (16 bits) sent, only the low 10 bits are valid as set for its size.
Coil
00029 00028 00027 00026 00025 00024 00023 00022 00021 00020
Status
0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1
z
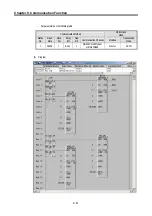
It’s supposed that GM7U main unit is the master and it writes word data continually on the Holding
Registers of the station no. 17, a Modicon product.
z
The master writes 000A and 0102 on the Holding Registers 40002 of the slave station no. 17. The data
that is to be written are saved in any array variable WR_DB1 of the 4 sized BYTE type.
Variable
Value to save
WR_DB1 [0]
2#00001010 or 16#0A
WR_DB1 [1]
2#00000000 or 16#00
WR_DB1 [2]
2#00000010 or 16#02
WR_DB1 [3]
2#00000001 or 16#01
z
The size of BYTE_CNT is the same as when the data to be written are converted by byte. The
above data are 2 words that need 4 bytes. Therefore the size of BYTE_CNT is 4.
z
Data is sent starting from the low word by byte unit. An example of sending the above data is as
follows.
Summary of Contents for GLOFA G7M-DR20U
Page 28: ...Chapter 4 Names of Parts 4 3 2 G7M DRT60U N 3 G7M DT60U N 4 G7M DT60U P...
Page 29: ...Chapter 4 Names of Parts 4 4 5 G7M DR60U DC 6 G7M DRT60U N DC 7 G7M DT60U N DC...
Page 31: ...Chapter 4 Names of Parts 4 6 3 G7M DT40U N 4 G7M DT40U P 5 G7M DR40U DC...
Page 32: ...Chapter 4 Names of Parts 4 7 6 G7M DRT40U N DC 7 G7M DT40U N DC 8 G7M DT40U P DC...
Page 33: ...Chapter 4 Names of Parts 4 8 4 1 3 30 point main unit 1 G7M DR30U 2 G7M DRT30U N 3 G7M DT30U N...
Page 34: ...Chapter 4 Names of Parts 4 9 4 G7M DT30U P 5 G7M DR30U DC 6 G7M DRT30U N DC...
Page 36: ...Chapter 4 Names of Parts 4 11 2 G7M DRT20U N 3 G7M DT20U N 4 G7M DT20U P...
Page 37: ...Chapter 4 Names of Parts 4 12 5 G7M DR20U DC 6 G7M DRT20U N DC 7 G7M DT20U N DC...
Page 38: ...Chapter 4 Names of Parts 4 13 8 G7M DT20U P DC...
Page 159: ...Chapter 7 Usage of Various Functions 7 52 c Program...
Page 183: ...Chapter 7 Usage of Various Functions 7 76 c Program...
Page 253: ...Chapter 8 Communication Functions 8 27 b When uses Ch 1 Built in RS 485...
Page 356: ...Appendix 1 System Definitions App1 9 6 Position Parameter...
Page 357: ...Appendix 1 System Definitions App1 10 7 High Speed Counter Parameter...