INTRODUCTION
PRELIMINAR STUDIES AND CONSIDERATIONS
MAINTENANCE AND DAMAGE PREVENTION
WORK ON BASIC VEHICLE
MOUNTING AND CONSTRUCTION
POWER TAKE-OFF
ELECTRIC AND ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS
APPENDIX
V1.0, February 2015
Body Builder Manual Part II, Specific Book LCV
51
There are some areas where the welding is not allowed. Do not weld on:
- The flanges of the beams except for changes on the wheelbase or on the rear
overhang.
- The stiffener and cross member gusset.
- Areas close to the airbag system or seat belts, which could result in their mal
-
functioning. These should be protected properly at all events.
- The engine, power train, axles, etc.
- The A- and B-pillars of the vehicle.
- The radii of curvature.
To get a proper weld, defects such as undercuts, fissure, blow holes, pits in the weld
seam, etc. should be avoided. If the welding bead is not good, it will result in stress
concentration that will have an effect on fatigue strength.
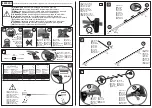
Examples of incorrect types of welded connections:
Fig. 4-36 LCV_SPBGC41_007 Faulty weld seams - samples
CAUTION
When welding, grinding or cutting near items such as brake lines, electrical cables,
etc., always take the necessary precautions for their protection, also considering
dismantling them, if necessary. Otherwise they could be damaged and not work
properly.
1
Crack
6
Lamella tearing
2
Crater
7
Over lap
3
Lack of penetration
8
Fisch eye
4
Lack of throat thickness
9
Under cut
5
Lack of angle