Page 10-25
As you can see, the rows that originally occupied positions 2 and 3 have been
swapped.
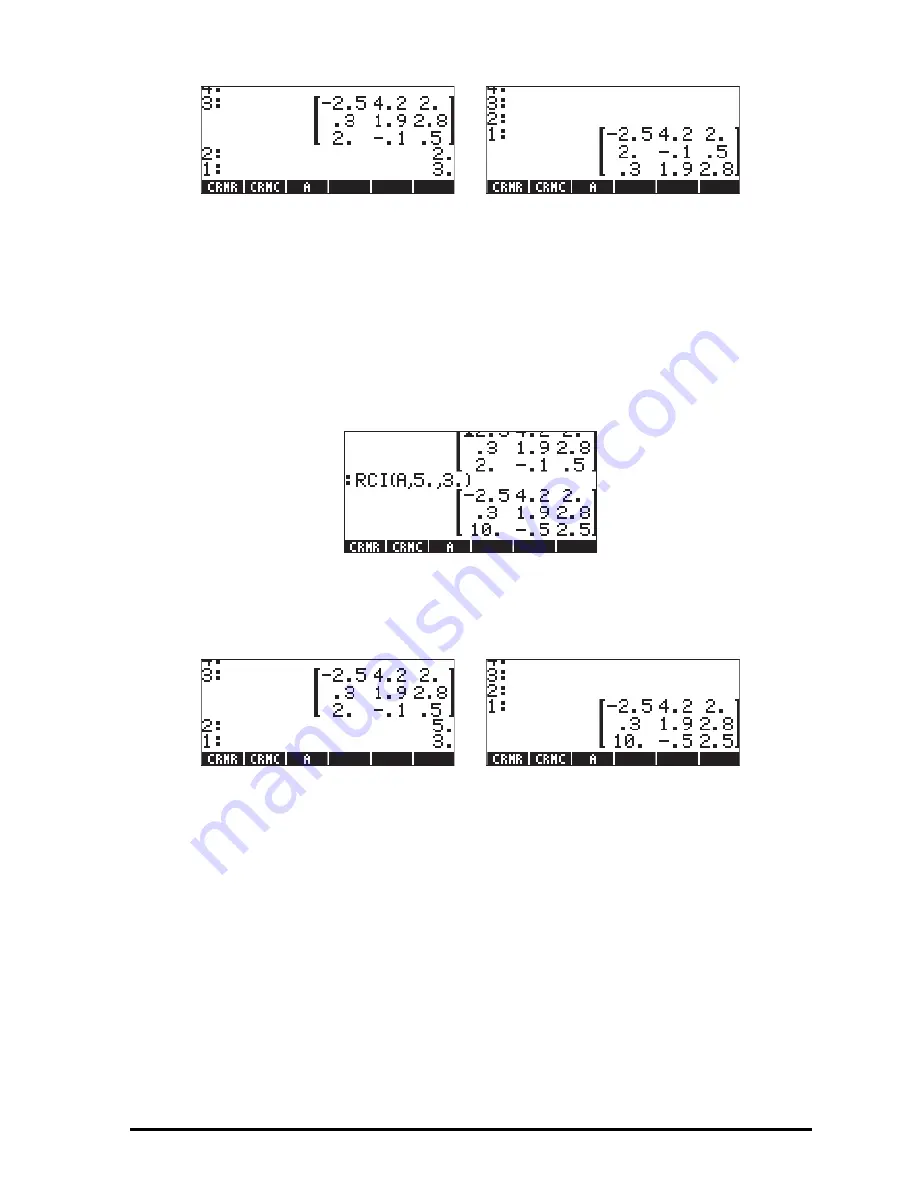
Function RCI
Function RCI stands for multiplying
R
ow I by a
C
onstant value and replace the
resulting row at the same location. The following example, written in ALG
mode, takes the matrix stored in A, and multiplies the constant value 5 into row
number 3, replacing the row with this product.
This same exercise done in RPN mode is shown in the next figure. The left-hand
side figure shows the setting up of the matrix, the factor and the row number, in
stack levels 3, 2, and 1. The right-hand side figure shows the resulting matrix
after function RCI is activated.
Function RCIJ
Function RCIJ stands for “take Row I and multiplying it by a constant C and then
add that multiplied row to row J, replacing row J with the resulting sum.” This
type of row operation is very common in the process of Gaussian or Gauss-
Jordan elimination (more details on this procedure are presented in a
subsequent Chapter). The arguments of the function are: (1) the matrix, (2) the
constant value, (3) the row to be multiplied by the constant in(2), and (4) the
row to be replaced by the resulting sum as described above. For example,
taking the matrix stored in variable A, we are going to multiply column 3 times
1.5, and add it to column 2. The following example is performed in ALG
mode:
Summary of Contents for 50G
Page 1: ...HP g graphing calculator user s guide H Edition 1 HP part number F2229AA 90006 ...
Page 130: ...Page 2 70 The CMDS CoMmanDS menu activated within the Equation Writer i e O L CMDS ...
Page 206: ...Page 5 29 LIN LNCOLLECT POWEREXPAND SIMPLIFY ...
Page 257: ...Page 7 20 ...
Page 383: ...Page 11 56 Function KER Function MKISOM ...
Page 715: ...Page 21 68 Whereas using RPL there is no problem when loading this program in algebraic mode ...
Page 858: ...Page L 5 ...






























