Page 9-21
3 - Use function
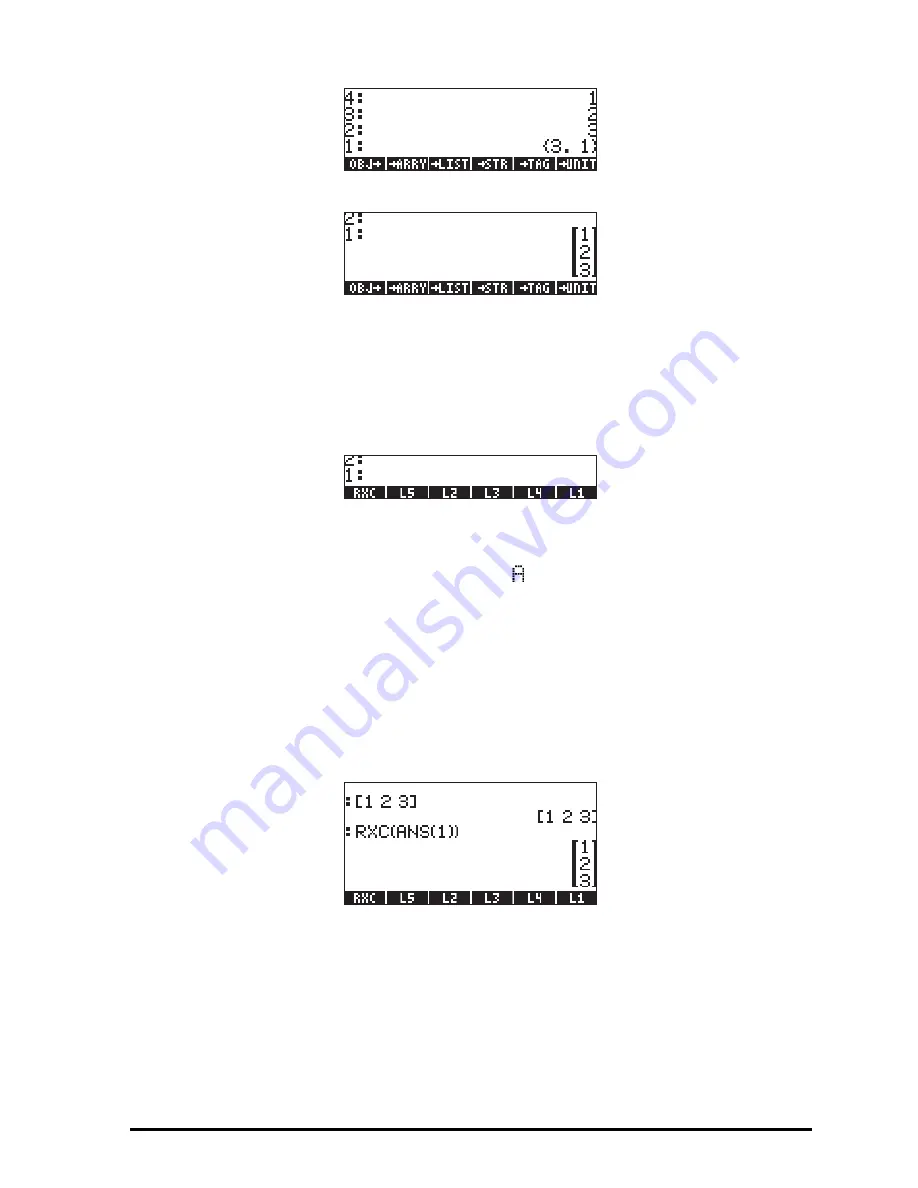
ARRY to build the column vector
These three steps can be put together into a UserRPL program, entered as
follows (in RPN mode, still):
‚å„°
@)TYPE! @OBJ
@
1 +
!
ARRY@
`³~~rxc` K
A new variable,
@@RXC@@
, will be available in the soft menu labels after pressing
J
:
Press
‚
@@RXC@@
to see the program contained in the variable RXC:
<< OBJ
1 +
RRY >>
This variable,
@@RXC@@
, can now be used to directly transform a row vector to a
column vector. In RPN mode, enter the row vector, and then press
@@RXC@@
. Try,
for example:
[1,2,3]
`
@@RXC@@
.
After having defined this variable , we can use it in ALG mode to transform a
row vector into a column vector. Thus, change your calculator’s mode to ALG
and try the following procedure:
[1,2,3]
` J
@@RXC@@
„ Ü „
î
, resulting in:
Transforming a column vector into a row vector
To illustrate this transformation, we’ll enter the column vector
[[1],[2],[3]]
in RPN mode. Then, follow the next exercise to transform
a row vector into a column vector:
1 - Use function OBJ
to decompose the column vector
Summary of Contents for 50G
Page 1: ...HP g graphing calculator user s guide H Edition 1 HP part number F2229AA 90006 ...
Page 130: ...Page 2 70 The CMDS CoMmanDS menu activated within the Equation Writer i e O L CMDS ...
Page 206: ...Page 5 29 LIN LNCOLLECT POWEREXPAND SIMPLIFY ...
Page 257: ...Page 7 20 ...
Page 383: ...Page 11 56 Function KER Function MKISOM ...
Page 715: ...Page 21 68 Whereas using RPL there is no problem when loading this program in algebraic mode ...
Page 858: ...Page L 5 ...






























