Chapter 7 Explanation of Functions
7 - 2
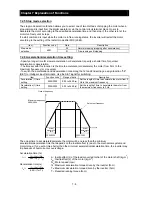
7.1.5 Intelligent input terminal status
When the intelligent input terminal status function (d005) is selected, the inverter displays the states of the
inputs to the intelligent input terminals.
The internal CPU of the inverter checks each intelligent input for significance, and the inverter displays
active inputs as those in the ON state. (*1)
Intelligent input terminal status is independent of the a/b contact selection for the intelligent input terminals.
(Example)
Intelligent input terminals [2], and [1]: ON
Intelligent input terminals [5], [4], and [3]: OFF
(*1)When input terminal response time is set, terminal recognition is delayed.
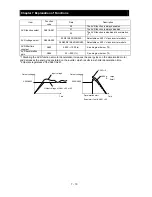
7.1.6 Intelligent output terminal status
When the intelligent output terminal status function (d006) is selected, the inverter displays the states of
the outputs from the intelligent output terminals.
This function does not monitor the states of the control circuit terminals but monitors those of the outputs
from the internal CPU.
Intelligent input terminal status is independent of the a/b contact selection for the intelligent input terminals.
(Example)
Intelligent output terminals [11]: ON
Alarm relay terminal AL : OFF
7.1.7 Scaled output frequency monitoring
When the scaled output frequency monitoring (d007) is selected, the inverter displays the gain data
converted from the output frequency with the frequency scaling conversion factor (b086).
Use this function, for example, to change the unit of a value (e.g., motor speed) on display.
Value displayed by function "d007" = "output frequency monitor(d001)" x "frequency scaling conversion
factor (b086)"
The frequency scaling conversion factor (b086) can be set within the range 0.01 to 99.99 in steps of 0.01.
(Example) Displaying the speed of a 4-pole motor
Speed N (min
-1
) = (120 x f [Hz])/pole = f (Hz) x 30
As the result of the above calculation with the factor (b086) set to 30.00, the inverter displays "1800"
(60 x 30.0) when the output frequency is 60 Hz.
(Display)
0.00 to 99.99 in steps of 0.01
100.0 to 999.9 in steps of 0.1
1000. to 9999. in steps of 1
1000 to 3996 in units of 10
Note: When you have selected the digital operator as the device to input frequency-setting commands and
Data change mode selection (b163=01), you can change the output frequency setting by using the
△
and/or
▽
key (only while the inverter is operating the motor).
- The change in output frequency made in this mode can be reflected in the frequency setting
(function "F001"). Press the STR key to write the new frequency over the currently selected
frequency setting. (The precision of the storable frequency data depends on the frequency
setting.)
- You cannot change the output frequency while the PID function is enabled or the inverter is not
operating the motor.
- When use UP/DWN function, please do not use it.
Display
: The segment is on,
indicating the ON state.
: The segment is off,
indicating the OFF state.
Intelligent input terminals
ON
OFF
11
(ON)
AL
(OFF)
Display
: The segment is on,
indicating the ON state.
: The segment is off,
indicating the OFF state.
Intelligent output terminals
ON
OFF
1
(ON)
2
(ON)
3
(OFF)
4
(OFF)
5
(OFF)
Summary of Contents for NES1-002LB
Page 9: ......
Page 21: ......
Page 25: ......
Page 28: ...Chapter 3 Exterior Views 3 3 ...
Page 30: ......
Page 35: ......
Page 53: ......
Page 75: ......
Page 154: ......
Page 196: ......
Page 203: ...Chapter 10 Troubleshooting This chapter describes the troubleshooting methods ...
Page 204: ......
Page 211: ......
Page 219: ......
Page 229: ......
Page 289: ...Appendix Appendix A Appendix A 1 ...
Page 290: ......
Page 292: ...Appendix Appendix 2 ...