101
CHAPTER 8: Testing Twisted-Pair Cable
8.5 Delay/Delay Skew
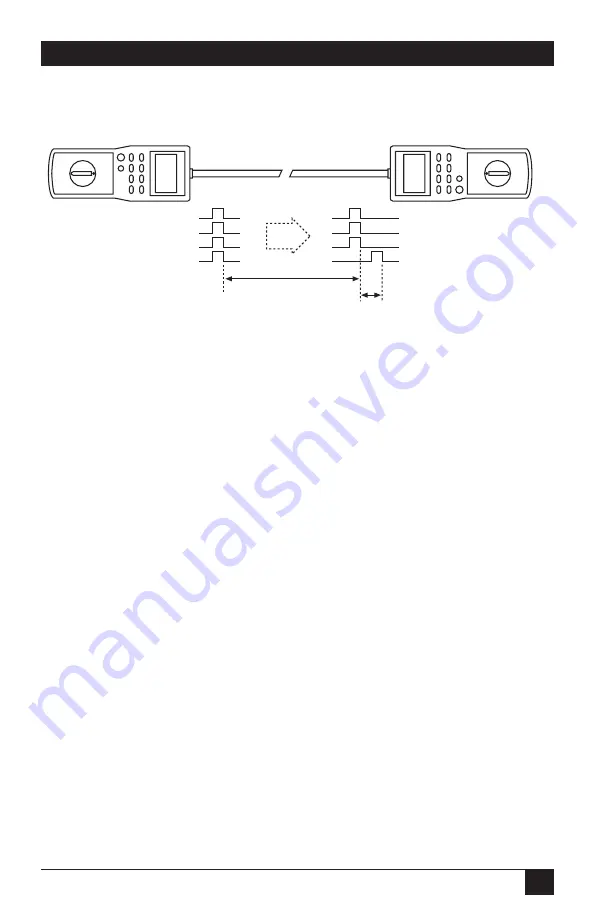
Delay is a measure of the time electrical signals take to propagate from one
end of the cable to the other end. The difference in propagation delays
from one cable pair to another is called Delay Skew.
Delay is important for the proper operation of many Local Area Networks,
particularly Ethernet. Because of the design of these networks, too much
delay can result in data re-transmissions, ultimately slowing down the
network.
Delay Skew is becoming increasingly important in emerging high-speed
networks such as 100BASET4, 622-Mbps ATM, and Gigabit Ethernet. To
transmit data at these rates, these emerging standards use all four cable
pairs while transmitting data. In order to recombine the data at the other
end of the cable, these standards require that the propagation delay of all
pairs be roughly equal. If there is too much difference in delay, or Delay
Skew, these LANs are unable to reconstruct the data.
Test Results
Possible Solutions
Too much Delay
NVP may be incorrect. Calibrate NVP and re-run the test.
or Delay Skew
Use a higher-grade cable; higher-grade cables typically have
lower propagation delays.
If your cable is identified as 2+2 or 3+1 cable, it may have
excessive Delay Skew. Contact your cable manufacturer.
Pair 1
Pair 2
Pair 3
Pair 4
Delay
Delay
Skew
Summary of Contents for SCAN-LAN VI
Page 2: ......
















































