ENGINE LUBRICATION
An improperly operating engine lubrication sys-
tem will quickly lead to engine seizure. Check the
engine oil level before each ride, and top off the oil
as described in Chapter Three. Oil pump service is
described in Chapter Five.
Oil Consumption High or
Engine Smokes Excessively
1. Worn valve guides.
2. Worn or damaged piston rings.
Excessive Engine Oil Leaks
1. Clogged air filter breather hose.
2. Loose engine parts.
3. Damaged gasket sealing surfaces.
Black Smoke
1. Clogged air filter.
2. Incorrect carburetor fuel level (too high).
3. Choke stuck open.
4. Incorrect main jet (too large).
White Smoke
1. Worn valve guide.
2. Worn valve oil seal.
3. Worn piston ring oil ring.
4. Excessive cylinder and/or piston wear.
Low Oil Pressure
1. Low oil level.
2. Damaged oil pump.
3. Clogged oil strainer screen.
4. Clogged oil filter.
5. Internal oil leak.
6. Incorrect type of engine oil being used.
7. Oil pressure relief valve stuck open.
High Oil Pressure
1. Incorrect type of engine oil being used.
2. Plugged oil filter, oil gallery or metering ori-
fices.
3. Oil pressure relief valve stuck closed.
No Oil Pressure
1. Damaged oil pump.
2. Excessively low oil level.
3. Damaged oil pump drive shaft.
4. Damaged oil pump drive sprocket.
5. Incorrect oil pump installation.
Low Oil Level
1. Oil level not maintained at correct level.
2. Worn piston rings.
3. Worn cylinder.
4. Worn valve guides.
5. Worn valve stem seals.
6. Piston rings incorrectly installed during engine
overhaul.
7. External oil leak.
8. Oil leaking into the cooling system.
Oil Contamination
1. Blown head gasket allowing coolant to leak into
the engine.
2. Water contamination.
3. Oil and filter not changed at specified intervals
or when operating conditions demand more fre-
quent changes.
42
CHAPTER TWO
6
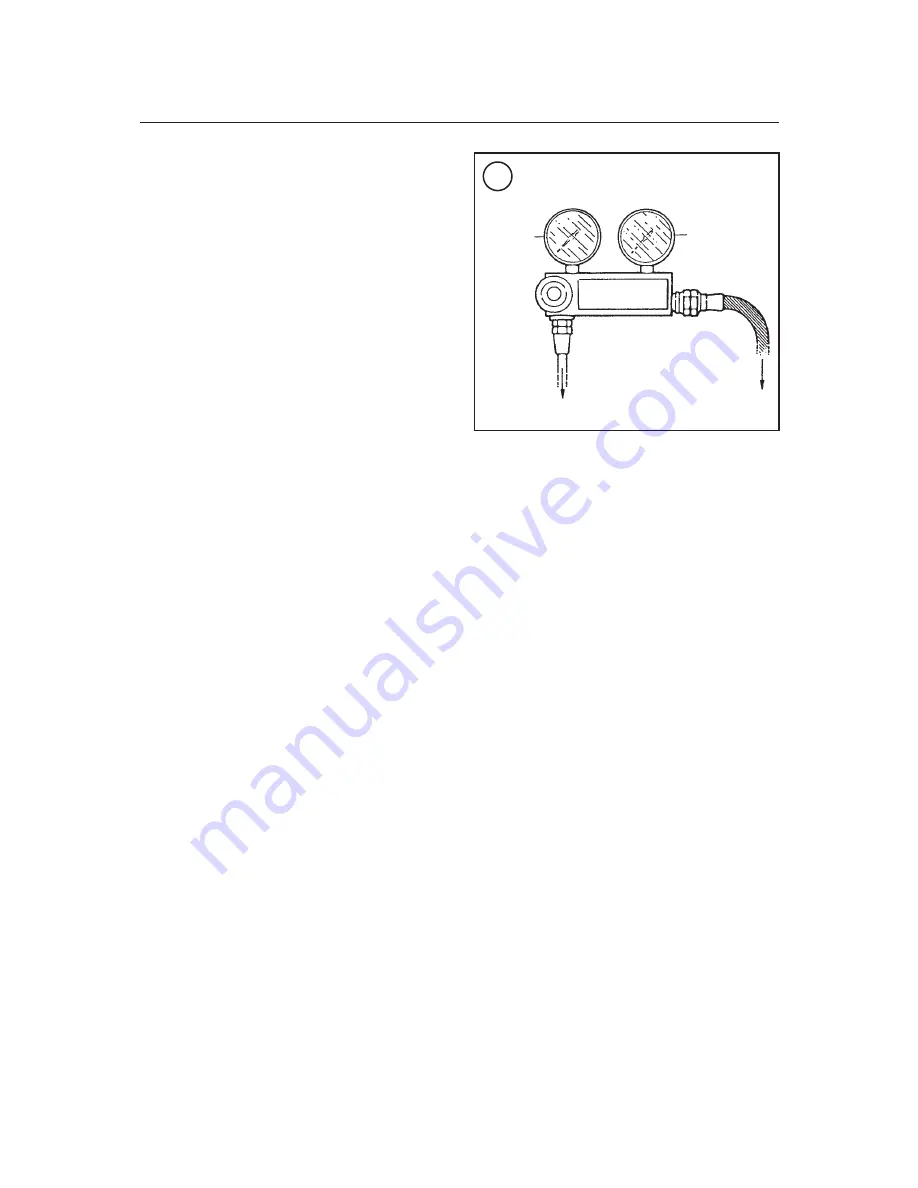
LEAKDOWN TESTER
Cylinder
pressure
Supply
pressure
To cylinder head
To air compressor






























