470
CN4093 Application Guide for N/OS 8.4
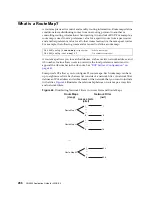
Neighbors and Adjacencies
In
areas
with
two
or
more
routing
devices,
neighbors
and
adjacencies
are
formed.
Neighbors
are
routing
devices
that
maintain
information
about
each
others’
health.
To
establish
neighbor
relationships,
routing
devices
periodically
send
hello
packets
on
each
of
their
interfaces.
All
routing
devices
that
share
a
common
network
segment,
appear
in
the
same
area,
and
have
the
same
health
parameters
(
hello
and
dead
intervals)
and
authentication
parameters
respond
to
each
other’s
hello
packets
and
become
neighbors.
Neighbors
continue
to
send
periodic
hello
packets
to
advertise
their
health
to
neighbors.
In
turn,
they
listen
to
hello
packets
to
determine
the
health
of
their
neighbors
and
to
establish
contact
with
new
neighbors.
The
hello
process
is
used
for
electing
one
of
the
neighbors
as
the
area’s
Designated
Router
(DR)
and
one
as
the
area’s
Backup
Designated
Router
(BDR).
The
DR
is
adjacent
to
all
other
neighbors
and
acts
as
the
central
contact
for
database
exchanges.
Each
neighbor
sends
its
database
information
to
the
DR,
which
relays
the
information
to
the
other
neighbors.
The
BDR
is
adjacent
to
all
other
neighbors
(including
the
DR).
Each
neighbor
sends
its
database
information
to
the
BDR
just
as
with
the
DR,
but
the
BDR
merely
stores
this
data
and
does
not
distribute
it.
If
the
DR
fails,
the
BDR
will
take
over
the
task
of
distributing
database
information
to
the
other
neighbors.
The Link-State Database
OSPF
is
a
link
‐
state
routing
protocol.
A
link
represents
an
interface
(or
routable
path)
from
the
routing
device.
By
establishing
an
adjacency
with
the
DR,
each
routing
device
in
an
OSPF
area
maintains
an
identical
Link
‐
State
Database
(LSDB)
describing
the
network
topology
for
its
area.
Each
routing
device
transmits
a
Link
‐
State
Advertisement
(LSA)
on
each
of
its
active
interfaces.
LSAs
are
entered
into
the
LSDB
of
each
routing
device.
OSPF
uses
flooding
to
distribute
LSAs
between
routing
devices.
Interfaces
may
also
be
passive
.
Passive
interfaces
send
LSAs
to
active
interfaces,
but
do
not
receive
LSAs,
hello
packets,
or
any
other
OSPF
protocol
information
from
active
interfaces.
Passive
interfaces
behave
as
stub
networks,
allowing
OSPF
routing
devices
to
be
aware
of
devices
that
do
otherwise
participate
in
OSPF
(either
because
they
do
not
support
it,
or
because
the
administrator
chooses
to
restrict
OSPF
traffic
exchange
or
transit).
When
LSAs
result
in
changes
to
the
routing
device’s
LSDB,
the
routing
device
forwards
the
changes
to
the
adjacent
neighbors
(the
DR
and
BDR)
for
distribution
to
the
other
neighbors.
OSPF
routing
updates
occur
only
when
changes
occur,
instead
of
periodically.
For
each
new
route,
if
an
adjacency
is
interested
in
that
route
(for
example,
if
configured
to
receive
static
routes
and
the
new
route
is
indeed
static),
an
update
message
containing
the
new
route
is
sent
to
the
adjacency.
For
each
route
removed
from
the
route
table,
if
the
route
has
already
been
sent
to
an
adjacency,
an
update
message
containing
the
route
to
withdraw
is
sent.
Содержание Flex System Fabric CN4093
Страница 27: ... Copyright Lenovo 2017 27 Part 1 Getting Started ...
Страница 28: ...28 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 58: ...58 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 72: ...72 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 85: ... Copyright Lenovo 2017 85 Part 2 Securing the Switch ...
Страница 86: ...86 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 98: ...98 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 112: ...112 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 136: ...136 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 156: ...156 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 192: ...192 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 228: ...228 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 229: ... Copyright Lenovo 2017 229 Part 4 Advanced Switching Features ...
Страница 230: ...230 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 298: ...298 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 382: ...382 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 392: ...392 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 416: ...416 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 452: ...452 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 466: ...466 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 496: ...496 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 508: ...508 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 510: ...510 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 514: ...514 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 538: ...538 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 539: ... Copyright Lenovo 2017 539 Part 7 Network Management ...
Страница 540: ...540 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 554: ...554 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 576: ...576 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 596: ...596 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 604: ...604 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 609: ... Copyright Lenovo 2017 609 Part 9 Appendices ...
Страница 610: ...610 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 626: ...626 CN4093 Application Guide for N OS 8 4 ...
Страница 633: ......
Страница 634: ...Part Number 00MY375 Printed in USA IP P N 00MY375 ...