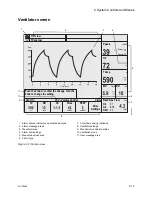
3 Operation
M1132382
3-13
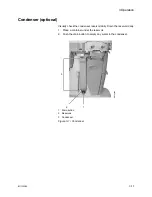
Active AGSS (optional)
WARNING
Always verify the proper operation of any gas scavenging
system; ensure the scavenging system is not occluded.
There are several versions of the optional active AGSS (Anesthesia
Gas Scavenging System) available depending on the hospital’s type
of waste gas disposal system.
Each version has a two-liter reservoir to capture peak exhaust flows
that briefly exceed the extract flow. Active scavenging systems
contain two relief valves to protect the patient from excess gas
pressure, or from the opposite situation, gas being drawn from the
breathing circuit.
The positive relief valve for the scavenging system is mounted on the
exhalation valve assembly. In the event that excess gas accumulates
in the scavenging system and cannot exit the machine properly,
pressure could build. If this pressure reaches 10 cmH2O, the positive
relief valve will be lifted up, allowing gas to escape into the room. This
prevents the pressure from backing up into the patient circuit.
The negative relief valve (which is located in the same place on all
scavenging receivers) serves to protect the patient in the event that
the extract flow exceeds system input flow. That is, it prevents gas
from being pulled out of the breathing circuit. If more than a small
amount of negative pressure (-0.3 cmH2O) is applied to the
scavenging system, the negative relief valve opens, allowing room air
to be drawn into the scavenging system instead of pulling gas from
the patient circuit. Its effectiveness is limited by the extract flow of the
particular active AGSS device:
•
The active low flow system is for use with high vacuum disposal
systems. It requires a vacuum system capable of a continuous
nominal flow of 36 l/min and 300 mmHg (12 inHg) or greater
vacuum pressure. A flow indicator on the system indicates when
the unit is in operation.
•
The active high flow system is for use with low vacuum (blower
type) disposal systems. This requires a system capable of
providing 50 to 80 l/min extract flow. A flow indicator on the
system indicates when the unit is in operation.
•
Another version is the active adjustable flow. It provides the
capability to adjust the flow with a needle valve (located in a
receiver beneath the breathing system) and a visual indicator bag
which should be properly inflated. It requires a vacuum system
capable of a continuous nominal flow of 36 l/min and 300 mmHg
(12 inHg) or greater vacuum pressure. The extract flow is limited
to 36 l/min and 300 mmHg (12 inHg) vacuum.
•
The active low flow system with a 12.7 mm hose barb connector
is for use with a low vacuum disposal system. It requires an
external venturi/ejector system with a flowmeter and a minimum
36 l/min extract flow.
Содержание Aespire View
Страница 1: ...Aespire View User s Reference Manual Software Revision 6 X...
Страница 16: ...Aespire View 1 8 M1132382...
Страница 46: ...Aespire View 3 16 M1132382...
Страница 50: ...Aespire View 4 4 M1132382...
Страница 88: ...Aespire View 7 8 M1132382...
Страница 112: ...Aespire View 9 10 M1132382...
Страница 114: ...Aespire View 10 2 M1132382 System pneumatic circuits Figure 10 1 Pneumatic circuit diagram AC 20 001...
Страница 118: ...Aespire View 10 6 M1132382 Electrical block diagram Figure 10 2 Electrical block diagram AC 20 008...
Страница 137: ...10 Specifications and Theory of Operation M1132382 10 25 Figure 10 9 Gas composition related errors AB 74 027...
Страница 148: ...Aespire View I 4 M1132382...