AWS Storage Gateway User Guide
EBS Volumes for EC2 Gateways
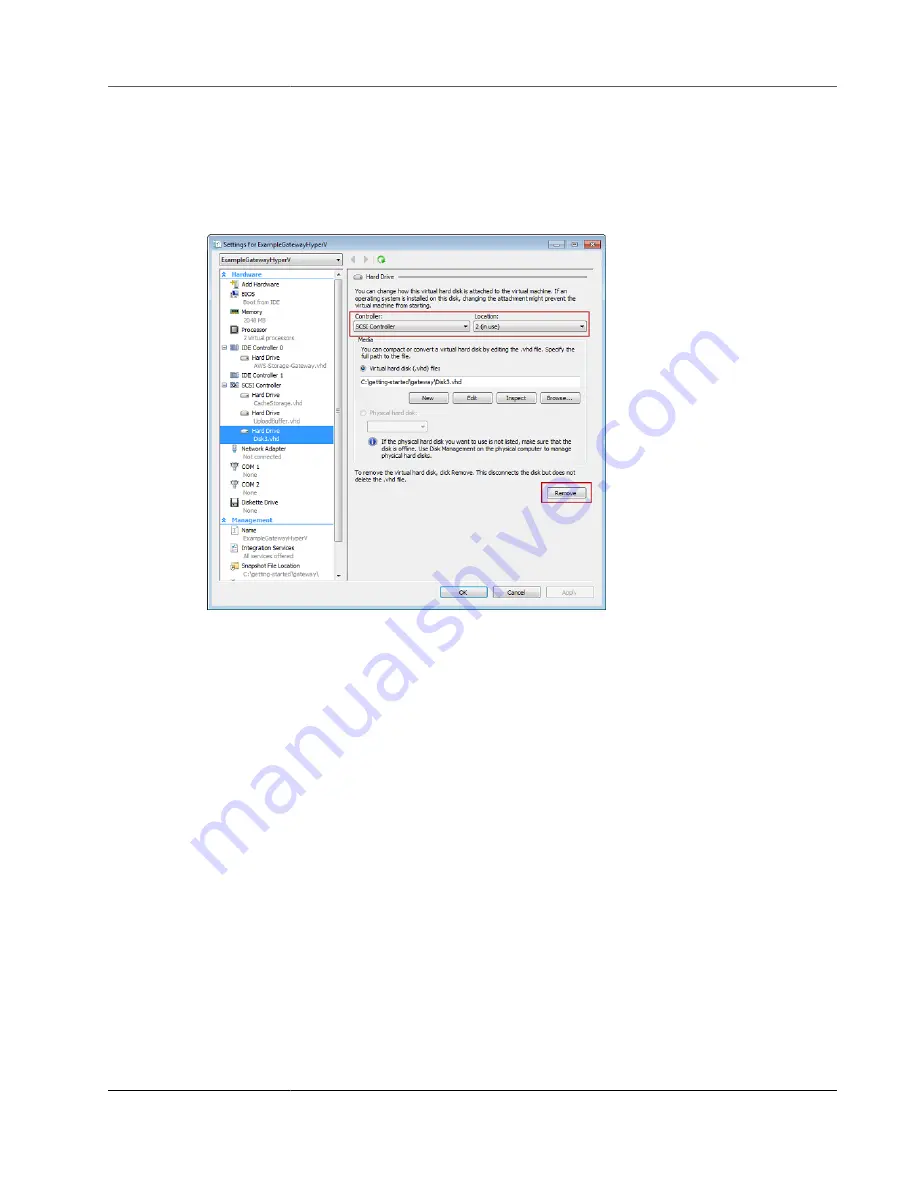
2. In the
Hardware
list of the
Settings
dialog box, select the disk to remove, and then choose
Remove
.
The disks you add to a gateway appear under the
SCSI Controller
entry in the
Hardware
list. Verify
that the
Controller
and
Location
value are the same value that you noted previously. Doing this
helps ensure that you remove the correct disk.
The first SCSI controller displayed in the Microsoft Hyper-V Manager is controller 0.
3. Choose
OK
to apply the change.
Adding and Removing Amazon EBS Volumes for Your
Gateway Hosted on Amazon EC2
When you initially configured your gateway to run as an Amazon EC2 instance, you allocated Amazon
EBS volumes for use as an upload buffer and cache storage. Over time, as your applications needs
change, you can allocate additional Amazon EBS volumes for this use. You can also reduce the storage
you allocated by removing previously allocated Amazon EBS volumes. For more information about
Amazon EBS, see
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
in the
Amazon EC2 User Guide for Linux
Instances
.
Before you add more storage to the gateway, you should review how to size your upload buffer and
cache storage based on your application needs for a gateway. To do so, see
Upload Buffer to Allocate (p. 221)
Determining the Size of Cache Storage to Allocate (p. 222)
There are limits to the maximum storage you can allocate as an upload buffer and cache storage. You
can attach as many Amazon EBS volumes to your instance as you want, but you can only configure these
volumes as upload buffer and cache storage space up to these storage limits. For more information, see
AWS Storage Gateway Limits (p. 395)
.
To add an Amazon EBS volume and configure it for your gateway
1. Create an Amazon EBS volume. For instructions, see
Creating or Restoring an Amazon EBS Volume
the
Amazon EC2 User Guide for Linux Instances
.
API Version 2013-06-30
356






























