64
Timing, IRIG-B and Pulses
7.4.8
Cable Delays
Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (C) in free space or vacuum and a fraction of that
speed through cabling. The speed of an electromagnetic wave in free space is given by Constant 7.6.
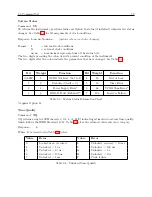
(7.6)
C
≈
9
.
84
×
10
8
f eet/second
Since electromagnetic waves travel slower through any cable, cable manufacturers normally specify
cable with a velocity factor (VF), which is a percentage of the speed of light in free space, and
characteristic of the specific cable. The velocity factor for the RG-6 cabling used by Arbiter Systems
for GPS antenna connections, is about 83% of C. Most transmission lines have velocity factors in
the range of 65% to 97%. Using these values you can determine the actual time delay in your cable
distribution system and compare it to your required accuracy. As an example, 840 feet of RG-6
cable (with a velocity factor of 83%) would delay the timing signal by one microsecond. For IRIG-B
timing applications, these delays may not be important, compared to other criteria. Otherwise,
you would be forced to compensate for the time delay using another method, such as advancing
the timing output or placing another master clock at the remote site.
7.4.9
Solutions
There are many solutions to providing an accurate timing signal to equipment in distant locations.
However, the most satisfying solution may not be to string cabling for hundreds of meters. The
costs associated with installing and maintaining cabling over a wide area may be unsatisfactory.
Since the GPS is so pervasive, it may prove to be less costly to install another clock at a distant
location, which would also improve accuracy and provide redundancy. Before installing cabling
over a wide area, be sure to first examine all the possibilities.
Содержание 1088A
Страница 4: ...iv ...
Страница 6: ...vi ...
Страница 18: ...xviii LIST OF FIGURES ...
Страница 23: ...1 4 Attaching Rack Mount Ears to 1088A B Series Clocks 3 Figure 1 2 Attaching Rack Mount Ears ...
Страница 24: ...4 Unpacking the Clock ...
Страница 32: ...12 Front and Rear Panels ...
Страница 38: ...18 Connecting Inlet Power Input and Output Signals ...
Страница 41: ...4 1 GPS Antenna Installation 21 Figure 4 2 Antenna Mounting Bracket Figure 4 3 Antenna Mounting with AS0044600 ...
Страница 46: ...26 GPS Antenna and Cable Information ...
Страница 48: ...28 Setting Internal Jumpers Figure 5 1 Model 1088B Main Board ...
Страница 76: ...56 The Setup Menus ...
Страница 112: ...92 Serial Communication and Command Set ...
Страница 127: ...B 4 Physical Dimensions 107 Figure B 1 Suggested Mounting of the AS0094500 Surge Arrester ...
Страница 128: ...108 Using Surge Arresters ...
Страница 137: ...C 5 Option 04 Parallel BCD Output 117 C 5 2 Option 04 Firmware Setup Figure C 2 Option 04 Firmware Setup ...
Страница 145: ...C 5 Option 04 Parallel BCD Output 125 Figure C 4 Option 04 Output Jumper Settings ...
Страница 146: ...126 Options List Figure C 5 Option 04 Board Layout and Jumper Locations ...
Страница 165: ...C 12 Option 17 Parallel BCD Output and Second RS 232 Port 145 Figure C 11 Option 17 Output Jumper Settings ...
Страница 166: ...146 Options List Figure C 12 Option 17 Board Layout and Jumper Locations ...
Страница 176: ...156 Options List C 14 5 Typical Network Configuration Figure C 15 Option 18 Network Configuration ...
Страница 187: ...C 16 Option 20A Four Fiber Optic Outputs 167 Figure C 22 Option 20A Jumper Locations ...
Страница 194: ...174 Options List Figure C 24 Option 23 Internal Jumper Setup ...
Страница 196: ...176 Options List Figure C 25 Option 27 Jumper Locations ...
Страница 214: ...194 Options List Figure C 28 Option 29 Connector Signal Locations ...
Страница 270: ...250 Options List ...