AMD2000 Series - Servo Drive - User Manual
122
DS619-0-00-0019 - Rev 0
ANCA Motion
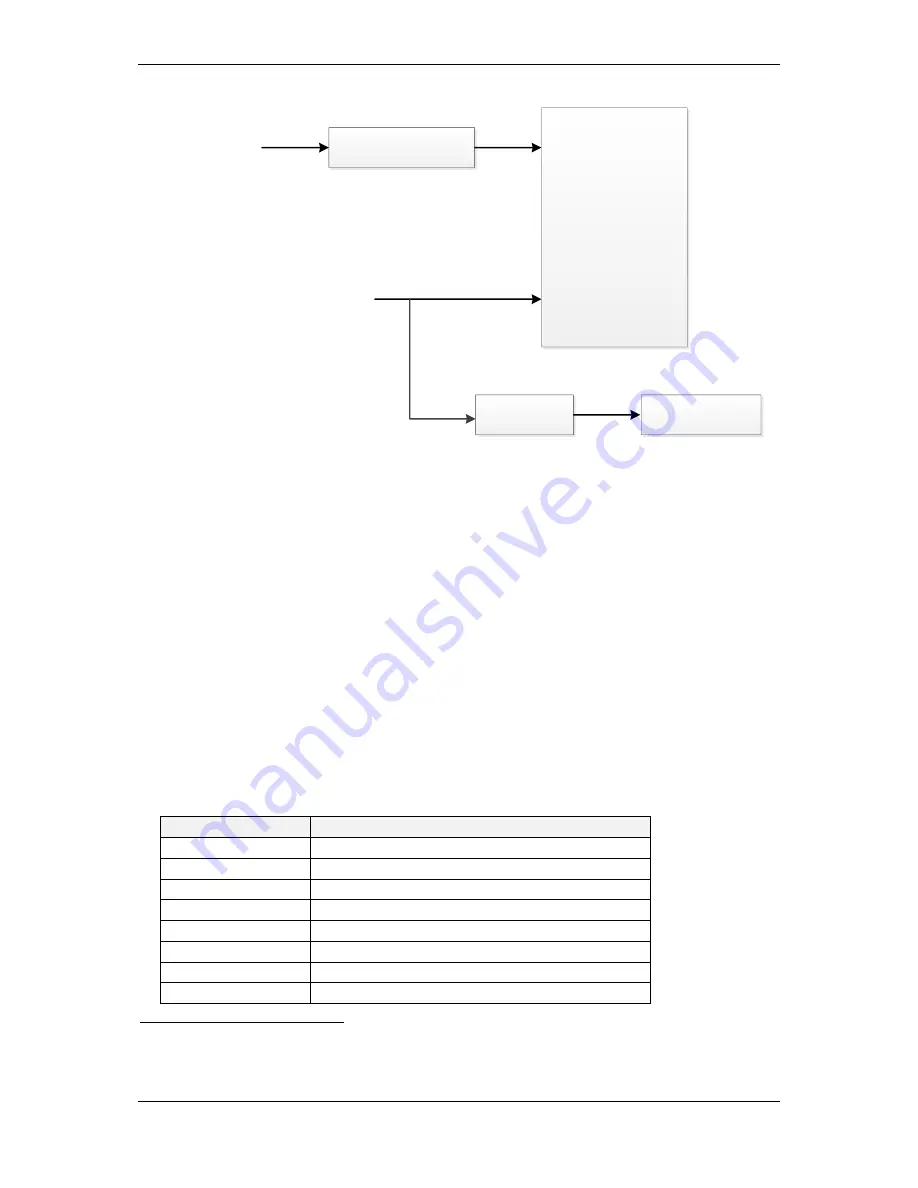
Demands
- position
- velocity
- acceleration
- torque/force
Constraints
Servo
Controller
Feedback/Estimates
- position
- velocity
- acceleration
- torque/force
Limits
C1D Errors
Figure 10-15 Overview of Motion Constraints and Limits
Global Constraints
Global constraints specify the minimum and maximum values associated with demands issued to the servo
control loops. In the case where a particular limit is not enabled, its global limit is set to the maximum internally
representable value.
7
The full set of adjustable constraints is listed below, and each of these constraints is
enabled by setting its associated bit to 1 (ON) in the Global Constraints Enable Flag (P-0-0099 / 32867). The
values residing in the following list of IDN’s, if so enabled, will be applied to constrain their associated demands;
IDN
Label
P-0-0099 / 32867
Global Constraints Enable Flag
P-0-0100 / 32868
Global Maximum Position Constraint
P-0-0101 / 32869
Global Minimum Position Constraint
P-0-0102 / 32870
Global Maximum Velocity Constraint
P-0-0103 / 32871
Global Minimum Velocity Constraint
P-0-0104 / 32872
Global Acceleration Constraint (positive velocity)
P-0-0105 / 32873
Global Acceleration Constraint (negative velocity)
P-0-0106 / 32874
Global Deceleration Constraint (positive velocity)
7
The AMD2000 used fixed integer representations internal to the drive, and these make scaling of these variables quite
important. Therefore even if the user hasn’t specified a constraint, there is always a global constraint due to the size of variable
that can be represented.
















































