6 Basic System Operation
6.3.4 Functions
6-20
6.3.4 Functions
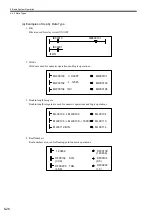
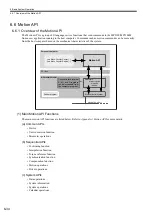
Functions are executed by being called from a parent, child, or grandchild drawing using the FSTART instruc-
tion.Unlike child and grandchild drawings, functions can be called from any drawing. The same function can also
be called simultaneously from drawings of different types and different hierarchies. Moreover, a function that
was previously created can also be called from another function.
The following advantages can be obtained by using functions:
• User programs can be easily divided into parts.
• User programs can be easily prepared and maintained.
Functions are divided into standard system functions, which are provided by the system, and user functions,
which are defined by the user.
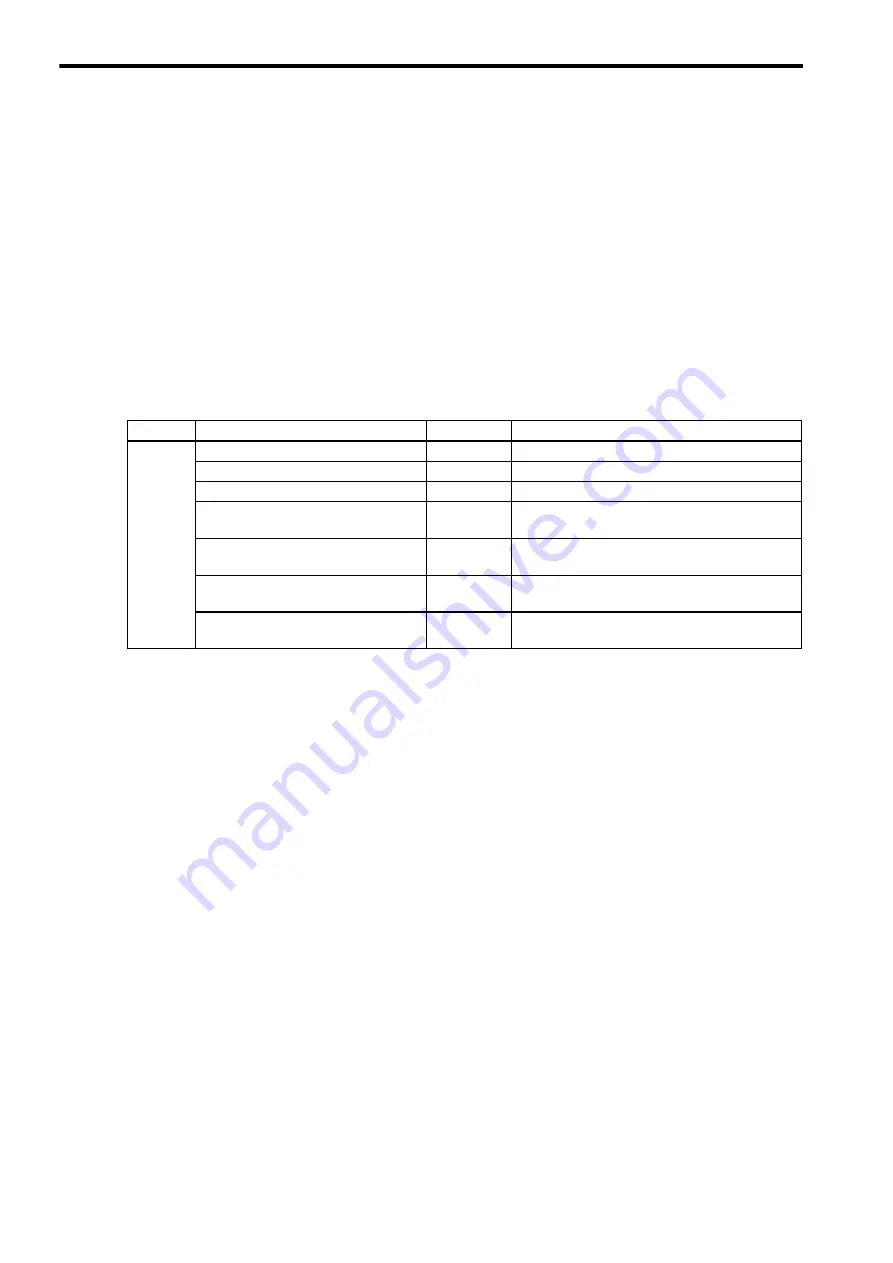
(1) Standard System Functions
The functions given in the following table, which include transfer functions, are provided by the system as stan-
dard functions. The user cannot change the standard system functions.
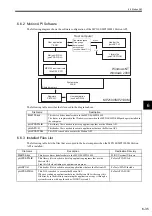
(2) User Functions
The body of the function (program) and the function definitions can be set by the user. The maximum number of
user functions is 500.
For details on MPE720 operating methods and details on instructions, refer to the relevant manuals.
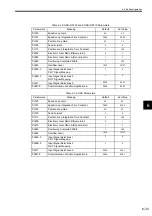
Type
Name
Symbol
Description
System
Functions
Counter
COUNTER
Up/down counter
First-in first-out
FINFOUT
First-in or first-out stack
Trace function
TRACE
Data trace execution control
Data trace read
DTRC-RD
Reading data from data trace memory to user mem-
ory
Inverter trace read
ITRC-RD
Reading data from inverter trace memory to user
memory
Send message function
MSG-SND
Sending a message to an external communication
device.
Receive message function
MSG-RCV
Receiving a message from an external communica-
tion device.