127
Configuring Switching Information
EdgeSwitch
™
Administration Guide
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Managing VLANs
Adding Virtual LAN (VLAN) support to a Layer-2 switch offers some of the benefits of both bridging and
routing. Like a bridge, a VLAN switch forwards traffic based on the Layer-2 header, which is fast, and like a
router, it partitions the network into logical segments, which provides better administration, security and
management of multicast traffic.
A VLAN is a set of end stations and the switch ports that connect them. You may have many reasons for the
logical division, such as department or project membership. The only physical requirement is that the end
station and the port to which it is connected both belong to the same VLAN.
Each VLAN in a network has an associated VLAN ID, which appears in the IEEE 802.1Q tag in the Layer-2 header
of packets transmitted on a VLAN. An end station may omit the tag, or the VLAN portion of the tag, in which
case the first switch port to receive the packet may either reject it or insert a tag using its default VLAN ID.
A given port may handle traffic for more than one VLAN, but it can only support one default VLAN ID.
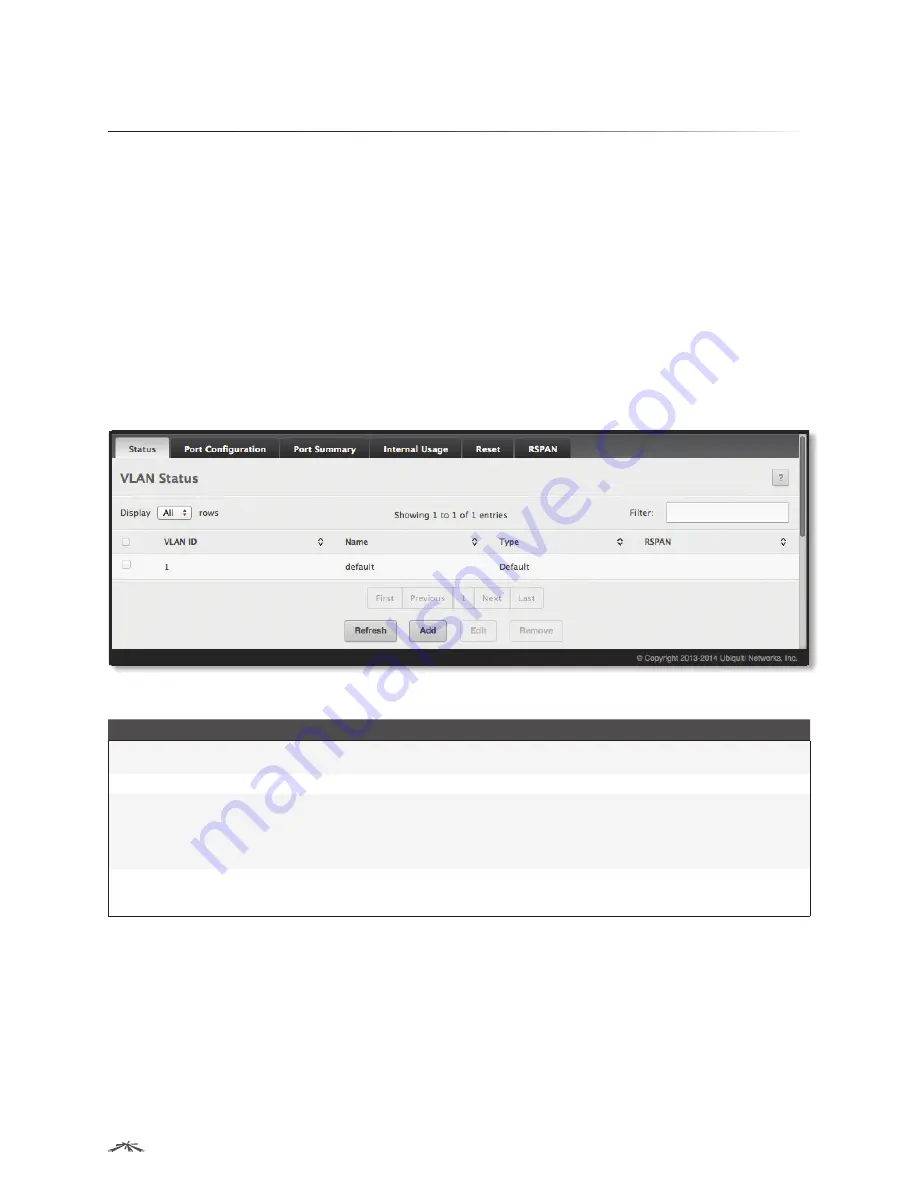
VLAN Status
Use the
VLAN Status
page to view information about the VLANs configured on your system. To access the
VLAN Status
page, click
Switching
>
VLAN
>
Status
in the navigation menu.
VLAN Status
VLAN Status Fields
Field
Description
VLAN ID
The VLAN Identifier (VID) of the VLAN. The range of the VLAN ID is
1
to
4093
. VLAN ID
1
is reserved for
the default VLAN which is always present and cannot be edited or removed.
Name
The name of the VLAN. VLAN ID 1 is always named
default
.
Type
The VLAN type, which can be one of the following:
•
Default
The default VLAN which is always present
•
Static
A VLAN that you have created and configured
•
Dynamic
A VLAN created by GVRP registration that you have not converted to static, and that
GVRP may therefore remove.
RSPAN
Displays
Enabled
if the VLAN is configured as the Remote Switched Port Analyzer (RSPAN) VLAN;
otherwise, blank. The RSPAN VLAN is used to carry mirrored traffic from source ports to a destination
probe port on a remote device.
Use the buttons to perform the following tasks:
• To add a VLAN, click
Add
. In the
Add VLAN
dialog box, specify the VLAN ID(s) in the
VLAN ID or Range
field
(use “
-
” or “
,
” to indicate a range of IDs or nonconsecutive IDs). Then, click
Submit
to apply the change.
• To configure a name for a VLAN or to convert a dynamic VLAN to a static VLAN, select the entry to modify
and click
Edit
; then, configure the desired VLAN settings and click
Submit
to apply the changes.
• To remove one or more configured VLANs, select each entry to delete, click
Remove
, and confirm the deletion.
• Click
Refresh
to refresh the page with the most current data from the switch.
To retain the changes across the switch’s next power cycle, click
System
>
Configuration Storage
>
Save
.






























