PMBus Slave Mode Command Examples
355
SNIU028A – February 2016 – Revised April 2016
Copyright © 2016, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PMBus Interface/I2C Interface
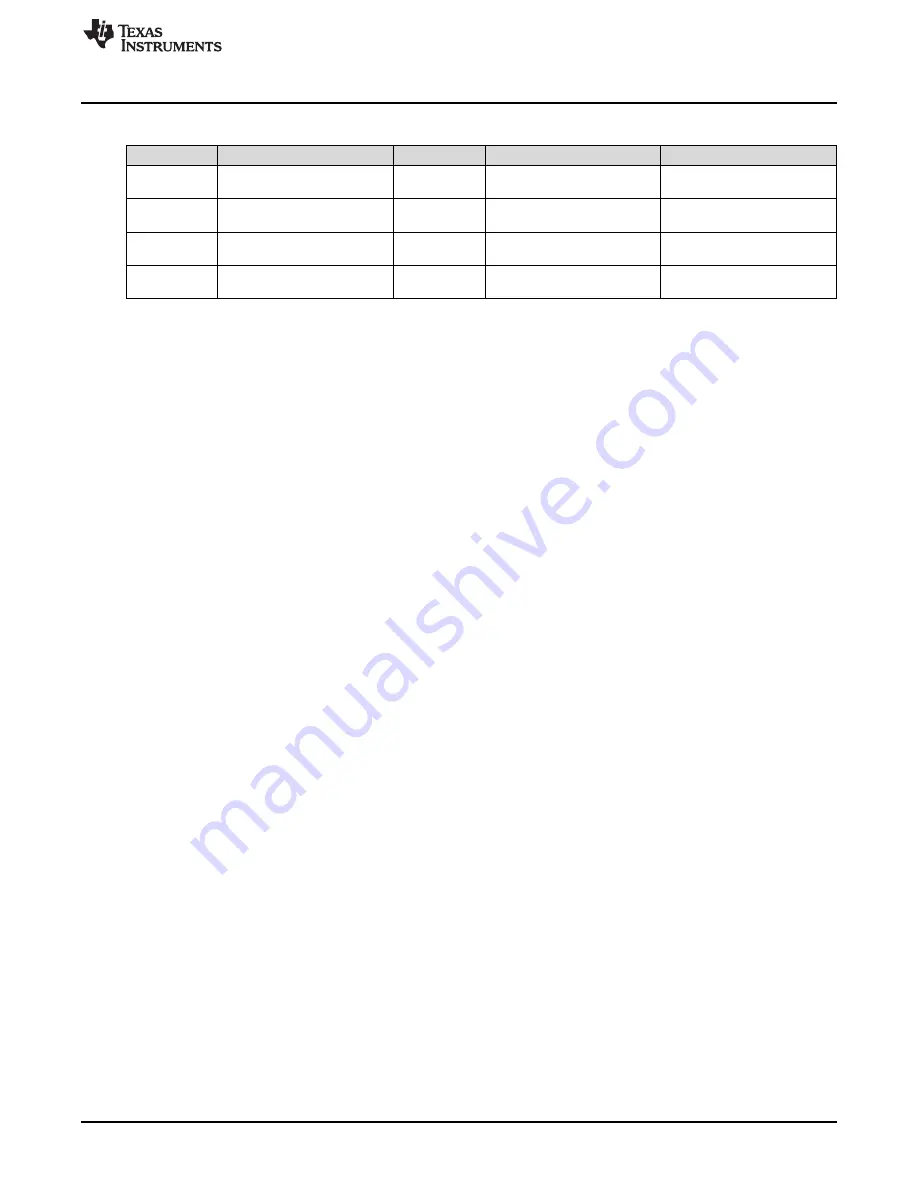
Table 10-1. (continued)
PMBST
PMBINTM
PMBCTRL3
Notes
UCD3138A
CLK_HIGH_TIMEOUT
CLK_HIGH_D
ETECT
CLK_HI_EN
High to enable
UCD3138064A CLK_HIGH_TIMEOUT
CLK_HIGH_D
ETECT
CLK_HI_EN
High to enable
UCD3138A64A CLK_HIGH_TIMEOUT
CLK_HIGH_TI
MEOUT
CLK_HI_DIS
Low to enable
UCD3138128A CLK_HIGH_TIMEOUT
CLK_HIGH_TI
MEOUT
CLK_HI_DIS
Low to enable
To enable clock high detection on the chips which support it, either set the CLK_HI_EN bit or clear the
CLK_HI_DIS bit in PMBCTRL3. If the PMBus Clock pin stays high for 50 msec in the middle of a message
to the UCD, the CLK_HIGH_TIMEOUT bit in PMBST will be set and the PMBus hardware will go to an idle
state and wait for a new message. To enable an interrupt, clear the bit in PMBINTM.
The 50 msec time is not an official PMBus specification, but it is a useful way to determine if the bus clock
is stuck high. With the hardware timeout detection, it is not necessary to use any firmware to detect
timeout.
10.3 PMBus Slave Mode Command Examples
The logic and timing of the PMBus interface is best explained by some examples of PMBus commands.
The detailed timing numbers are in
10.3.1 Write Command (Send Byte), No PEC
This is the simplest PMBus command, requiring only 2 bytes. The messages will first be shown with all
auto acknowledgement enabled. With auto-acknowledgement, this message and all short write messages
can be handled with one short sequence of code, executed once per message. The start of the next
message is included in the drawing. This shows the timing requirements if a second message follows with
no delay.
















































