Communication parameter group 07
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION 123
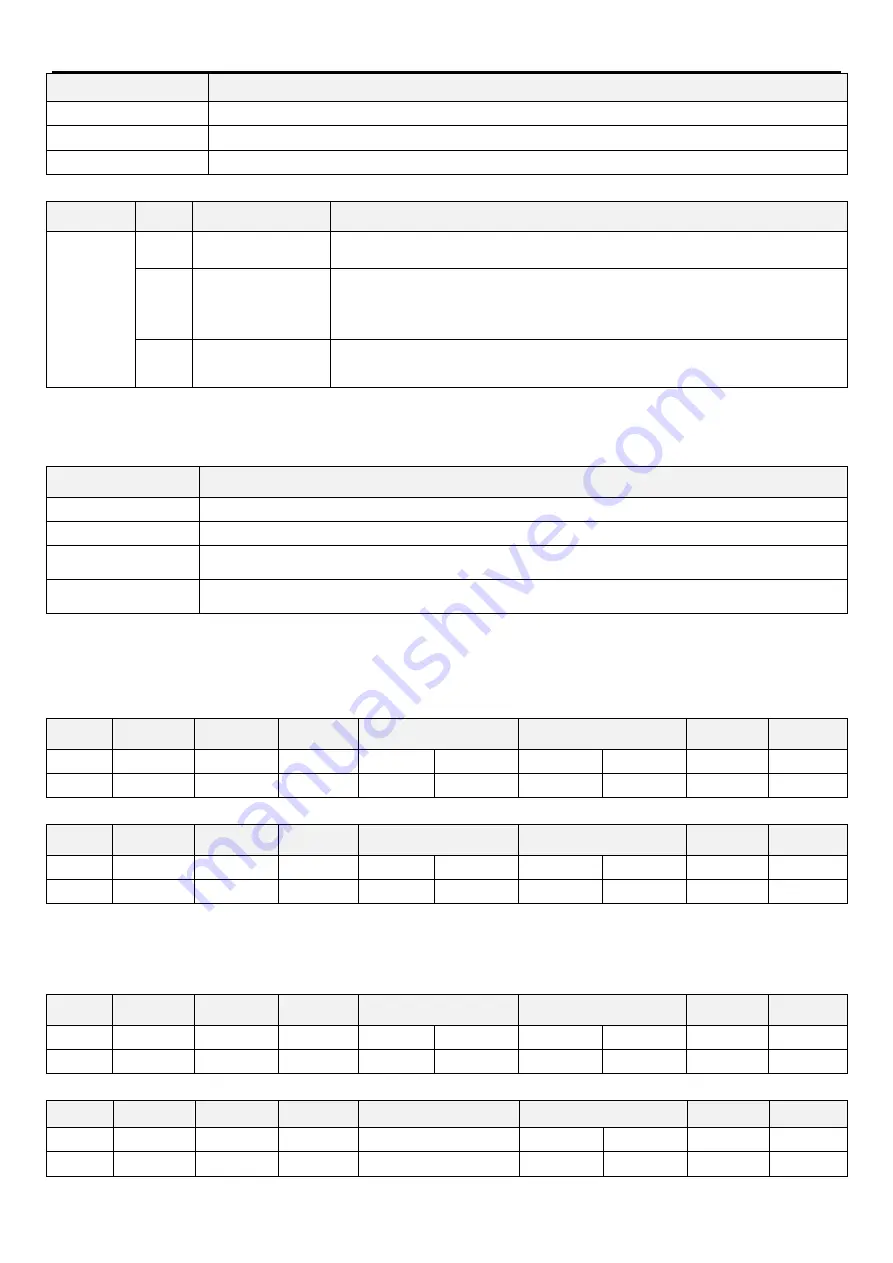
Message
Content
*1) Address
Set the address for sending information
*2) Function code
Function code set by Master+H80
*3)Error code
Set code in the following table
Error code list:
Source
Code Meaning
Remarks
Slave reply
H01
illegal function code
In query information sent by Master, the function code cannot be processed by slave
device. Function codes are not H03, H06, H08, H10 (Suppose).
H02
illegal data address
In query information sent by Master, the address cannot be processed by Slave
(outside the addresses listed in the table, the reserved parameters, the parameters
not allowed to be read, the parameters not allowed to be written).
H03
illegal data value
In query information sent by Master, the data cannot be processed by the Slave
(outside parameter writing range, required specified mode, other error, etc.).
Note: When read multiple parameters, it is not an error even if they are reserved parameters.
In data sent by Master, Slave (inverter) will detect the following errors, but will not respond when it detects the error.
Error detection item table:
Error item
Error content
Parity error
The parity test for data received by the inverter is different from the parity test set at the initial stage.
Frame error
The stop byte of the data received by the inverter mismatches the stop byte set at the initial stage.
Overflow error
When the inverter is receiving data, the host computer sends the next set of data before the inverter
finishes receiving the current one.
Error test
The LRC/CRC calculated by the inverter according to the received data is different from the received
LRC/CRC.
Communication example
Example 1. CU operation mode written by communication
Step 1: Upper controller modifies operation mode of inverter
Mode
Start
Address
Function Start address
Write data
Check
Stop
ASCII
H3A
H30 H31
H30 H36
H31 H30
H30 H30
H30 H30
H30 H30
H45 H39
0D 0A
RTU
>=10ms
01
06
10
00
00
00
8D 0A
>=10ms
Step 2: After receiving and processing the data without error, inverter will send a reply to upper controller
Mode
Start
Address
Function Start address
Write data
Check
Stop
ASCII
H3A
H30 H31
H30 H36
H31 H30
H30 H30
H30 H30
H30 H30
H45 H39
0D 0A
RTU
>=10ms
01
06
10
00
00
00
8D 0A
>=10ms
Example 2. Read parameter 01-28(P.162)value by upper controller
Step 1: Upper controller sends message to inverter to read 01-28(P.162) value. 01-28(P.162) address is
H00A2。
Mode
Start
Address
Function Start address
Number of registers
Check
Stop
ASCII
H3A
H30 H31
H30 H33
H30 H30
H41 H32
H30 H30
H30 H31
H35 H39
0D 0A
RTU
>=10ms
01
03
00
A2
00
01
25 E8
>=10ms
Step 2: After receive and processing the data without error, inverter will send 01-28(P.162) to upper controller
Mode
Start
Address
Function Number of data read
Read data
Check
Stop
ASCII
H3A
H30 H31
H30 H33
H30 H32
H46 H46
H46 H46
H46 H43
0D 0A
RTU
>=10ms
01
03
02
FF
FF
B9 F4
>=10ms
Summary of Contents for SL3 Series
Page 2: ......
Page 107: ......
Page 200: ...Appendix 4 Optional equipment Appendix 196 ...
Page 210: ...Appendix 5 European Specification Compatibility Description Appendix 206 ...
















































