GL.4
SEL-787 Relay
Instruction Manual
Date Code 20081022
Glossary
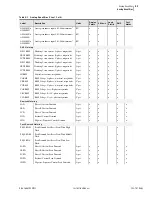
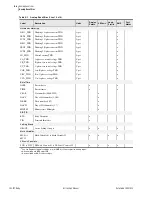
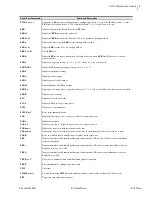
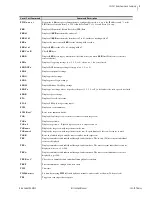
M
IRRORED
B
ITS
–Relay Word Bit
M
IRRORED
B
ITS
Protocol for direct relay-to-relay communications.
NEMA
Abbreviation for National Electrical Manufacturers Association.
Neutral
Overcurrent Element
A protection element that causes the relay to trip when the neutral current
magnitude (measured by the IN input) exceeds a user settable value. Used to
detect and trip in response to ground faults.
Nominal Frequency
Normal electrical system frequency, usually 50 or 60 Hz.
Nonfail-Safe
Refers to an output contact that is not energized during normal relay
operation. When referred to a trip output contact, the protected equipment
remains in operation unprotected when relay power is removed or if the relay
fails.
Nonvolatile Memory
Relay memory that is able to correctly maintain data it is storing even when
the relay is de-energized.
Overfrequency Element
A protection element that causes the relay to trip when the measured electrical
system frequency exceeds a settable frequency.
Phase Rotation
The sequence of voltage or current phasors in a multi-phase electrical system.
In an ABC phase rotation system, the B-phase voltage lags the A-phase
voltage by 120 degrees, and the C-phase voltage lags B-phase voltage by 120
degrees. In an ACB phase rotation system, the C-phase voltage lags the A-
phase voltage by 120°, and the B-phase voltage lags the C-phase voltage by
120 degrees.
Pickup Time
The time measured from the application of an input signal until the output
signal asserts. The time can be settable, as in the case of a logic variable timer,
or can be a result of the characteristics of an element algorithm, as in the case
of an overcurrent element pickup time.
Pinout
The definition or assignment of each electrical connection at an interface.
Typically refers to a cable, connector, or jumper.
Power, P
Real part of the complex power (S) expressed in units of Watts (W), kilovolt-
watts (kW), or megawatts (MW).
Power Factor
The cosine of the angle by which phase current lags phase voltage in an ac
electrical circuit. Power factor equals 1.0 for power flowing to a resistive load.
Power, Q
Reactive part of the complex power (S) expressed in units of Vars (W),
kilovars (kVar), or megavars (MVar).
PT
Abbreviation for potential transformer. Also referred to as a voltage
transformer or VT.
RAM
Abbreviation for Random Access Memory. Volatile memory where the relay
stores intermediate calculation results, Relay Word bits, and other data that are
updated every processing interval.
Relay Word
The collection of relay element and logic results. Each element or result is
represented by a unique identifier, known as a Relay Word bit.
Relay Word Bit
A single relay element or logic result that the relay updates once each
processing interval. A Relay Word bit can be equal to either logical 1 or
logical 0. Logical 1 represents a true logic condition, picked up element, or
Summary of Contents for SEL-787
Page 1: ...20081022 SEL 787 Transformer Protection Relay Instruction Manual PM787 01 NB ...
Page 6: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 12: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 18: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 78: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 206: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 280: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 334: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 376: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 388: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 474: ...This page intentionally left blank ...
Page 508: ...This page intentionally left blank ...