CHAPTER 13 A/D CONVERTER
Preliminary User’s Manual U17260EJ3V1UD
307
13.3 Registers Used in A/D Converter
The A/D converter uses the following six registers.
•
A/D converter mode register (ADM)
•
A/D port configuration register (ADPC)
•
Analog input channel specification register (ADS)
•
Port mode register 2 (PM2)
•
10-bit A/D conversion result register (ADCR)
•
8-bit A/D conversion result register (ADCRH)
(1) A/D converter mode register (ADM)
This register sets the conversion time for analog input to be A/D converted, and starts/stops conversion.
ADM can be set by a 1-bit or 8-bit memory manipulation instruction.
Reset signal generation sets this register to 00H.
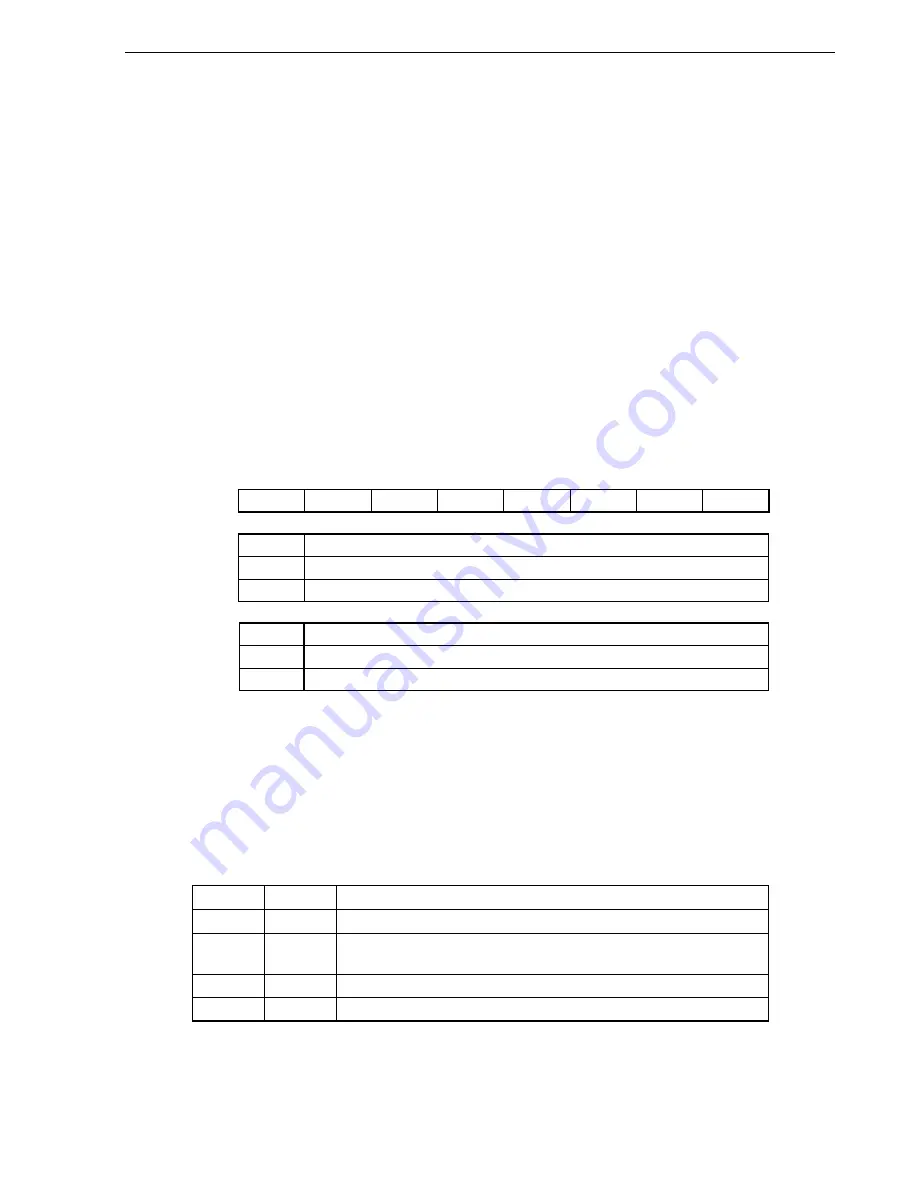
Figure 13-3. Format of A/D Converter Mode Register (ADM)
ADCE
LV0
Note 1
LV1
Note 1
FR0
Note 1
FR1
Note 1
FR2
Note 1
0
ADCS
A/D conversion operation control
Stops conversion operation
Enables conversion operation
ADCS
0
1
<0>
1
2
3
4
5
6
<7>
ADM
Address: FF28H After reset: 00H R/W
Symbol
Comparator operation control
Note 2
Stops comparator operation
Enables comparator operation (comparator: 1/2AV
REF
operation)
ADCE
0
1
Notes 1.
For details of FR2 to FR0, LV1, LV0, and A/D conversion, see
Table 13-2 A/D Conversion Time
Selection
.
2.
The operation of the comparator is controlled by ADCS and ADCE, and it takes 1
µ
s from operation
start to operation stabilization. Therefore, when ADCS is set to 1 after 1
µ
s or more has elapsed from
the time ADCE is set to 1, the conversion result at that time has priority over the first conversion
result. Otherwise, ignore data of the first conversion.
Table 13-1. Settings of ADCS and ADCE
ADCS ADCE
A/D
Conversion Operation
0
0
Stop status (DC power consumption path does not exist)
0 1
Conversion waiting mode (comparator: 1/2AV
REF
operation, only comparator
consumes power)
1
0
Conversion mode (comparator operation stopped
Note
)
1
1
Conversion mode (comparator: 1/2AV
REF
operation)
Note
Ignore data of the first conversion because it is not guaranteed range.
















































