User
Guide
for
Axoclamp
900A
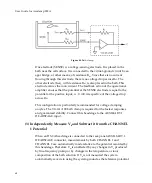
An
electrically
stable
bath
(reference)
electrode.
Perfusion
Normally
the
external
solution
used
in
vitro
experiments
is
a
pH
‐
buffered
salt
solution
that
mimics
the
extra
‐
or
intracellular
composition
of
the
cells
under
study.
Sometimes
the
solution
is
bubbled
with
CO
2
(to
maintain
the
pH
of
bicarbonate
‐
buffered
solutions)
and/or
O
2
(to
maintain
the
metabolic
viability
of
the
cells).
Some
cells
(
e
.g.,
those
in
retinal
slices)
have
unusually
high
metabolic
rates
and
require
fast
perfusion
with
high
‐
O
2
solution
to
remain
viable.
Other
cells
(
e
.g.,
neurons
in
dissociated
cell
culture)
may
not
need
any
perfusion
or
bubbling
at
all.
Because
the
health
of
the
cells
is
the
single
most
important
factor
in
determining
the
success
of
your
experiments,
it
is
worth
spending
some
time
establishing
the
optimal
conditions
for
cell
survival.
Mechanical
Stability
Sharp
microelectrode
recordings
are
not
robust
in
the
presence
of
vibrations,
and
neither
are
they
tolerant
of
large
drifts
in
the
tissue
or
electrode
that
tend
to
pull
the
electrode
out
of
the
cell.
For
this
reason,
it
is
important
to
use
a
good,
drift
‐
free
micromanipulator
for
the
electrode,
and
to
secure
the
tissue
or
cells
in
the
chamber
so
they
cannot
move
very
far.
Tissue
slices
are
commonly
held
in
place
in
the
chamber
by
a
weighted
“net”
or
“grid”
of
fine
threads.
A
grid
is
easily
made
as
follows.
Bend
a
piece
of
0.2–0.4
mm
diameter
platinum
wire
into
a
ring
small
enough
to
fit
in
the
bottom
of
your
chamber,
then
flatten
the
wire
in
a
vise.
Using
a
pair
of
fine
forceps,
pull
a
single
strand
of
nylon
thread
off
a
~1
m
length
of
unwaxed
nylon
dental
floss.
(It
is
very
wispy
but
remarkably
strong.)
Wrap
the
thread
tightly
in
a
spiral
around
a
strip
of
thin
black
card
about
3
×
10
cm,
securing
each
end
with
sticky
tape.
Bending
the
card
slightly,
slip
the
flattened
platinum
ring
under
the
threads,
and
adjust
its
position
and
the
spacing
of
the
threads
until
the
optimal
grid
pattern
is
obtained.
Finally,
add
a
tiny
spot
of
cyanoacrylate
glue
to
each
thread
crossing
point
and,
after
it
is
dry,
cut
the
completed
grid
free.
60