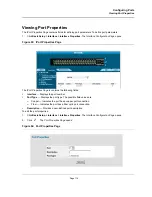
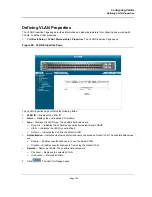
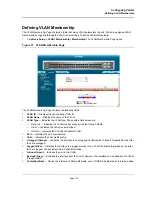
Configuring Ports
Page 112
•
Duplex Mode
— Displays the port duplex mode. This field is configurable only when auto negotiation is dis-
abled, and the port speed is set to 10M or 100M. This field cannot be configured on LAGs. The possible field
values are:
–
Full
— The interface supports transmission between the device and its link partner in both directions
simultaneously.
–
Half
— The interface supports transmission between the device and the client in only one direction at a
time.
•
Auto Negotiation
— Displays the auto negotiation status on the port. Auto negotiation is a protocol between
two link partners that enables a port to advertise its transmission rate, duplex mode, and flow control abilities
to its partner.
•
Advertisement
— Defines the auto negotiation setting the port advertises. The possible field values are:
–
Max Capability
— Indicates that all port speeds and duplex mode settings are accepted.
–
10 Half
— Indicates that the port advertises for a 10 Mbps speed port and half duplex mode setting.
–
10 Full
— Indicates that the port advertises for a 10 Mbps speed port and full duplex mode setting.
–
100 Half
— Indicates that the port advertises for a 100 Mbps speed port and half duplex mode setting.
–
100 Full
— Indicates that the port advertises for a 100 Mbps speed port and full duplex mode setting.
–
1000 Full
— Indicates that the port advertises for a 1000 Mbps speed port and full duplex mode setting.
–
1000 Half
— Indicates that the port advertises for a 1000 Mbps speed port and half duplex mode setting.
•
Back Pressure
— Displays the back pressure mode on the Port. Back pressure mode is used with half
duplex mode to disable ports from receiving messages.
•
Flow Control
— Displays the flow control status on the port. Operates when the port is in full duplex mode.
•
MDI/MDIX
— Displays the MDI/MDIX status on the port. Hubs and switches are deliberately wired opposite
the way end stations are wired, so that when a hub or switch is connected to an end station, a straight through
Ethernet cable can be used, and the pairs are matched up properly. When two hubs or switches are con-
nected to each other, or two end stations are connected to each other, a crossover cable is used to ensure
that the correct pairs are connected. The possible field values are:
–
Auto
— Use to automatically detect the cable type.
–
MDI (Media Dependent Interface)
— Use for end stations.
–
MDIX (Media Dependent Interface with Crossover)
— Use for hubs and switches.
•
LAG
— Indicates whether the port is part of a
Link Aggregation Group
(LAG).
The Interface Configuration LAG table contains the following fields:
•
LAG
— Indicates whether the port is part of a
Link Aggregation Group
(LAG).
•
LAG
Type
— Indicates the type of LAG defined by the first port assigned to the LAG. For example, 100-Cop-
per, or 100-Fiber.
•
LAG
Status
— Indicates whether the LAG is up or down.
•
LAG
Speed
— Displays the configured aggregated rate for the LAG. The possible field values are:
–
10
— Indicates the port is currently operating at 10 Mbps.
–
100
— Indicates the port is currently operating at 100 Mbps.
–
1000
— Indicates the port is currently operating at 1000 Mbps.
•
Auto
Negotiation
— Displays the auto negotiation status of the LAG. Auto negotiation is a protocol between
two link partners that enables a port to advertise its transmission rate, duplex mode, and flow control abilities
to its partner.
•
Back Pressure
— Displays the back pressure mode on the LAG. Back pressure mode is used with half
duplex mode to disable ports in the LAG from receiving messages.
•
Flow
Control
— Displays the flow control status of the LAG.
Summary of Contents for DXS-3250 - xStack Switch - Stackable
Page 9: ...Preface Intended Audience Page 8 ...
Page 274: ......
Page 275: ......
Page 285: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 278 ...
Page 286: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 279 ...
Page 287: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 280 ...
Page 288: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 281 ...
Page 289: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 282 ...
Page 290: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 283 ...
Page 291: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 284 ...
Page 292: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 285 ...
Page 293: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 286 ...
Page 294: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 287 ...
Page 295: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 288 ...
Page 296: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 289 ...
Page 297: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 290 ...
Page 298: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 291 ...
Page 299: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 292 ...
Page 300: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 293 ...
Page 301: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 294 ...
Page 302: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 295 ...
Page 303: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 296 ...
Page 304: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 297 ...
Page 305: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 298 ...
Page 306: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 299 ...
Page 307: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 300 ...
Page 308: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 301 ...
Page 309: ...Contacting D Link Technical Support Page 302 ...
Page 310: ...D Link DXS 3250 DXS 3227P DXS 3227 User Guide Page 303 ...