Page 2–4
2101510 Rev. AG
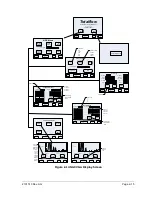
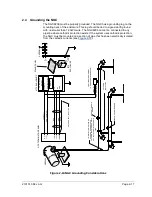
2.2 Processing a Sample
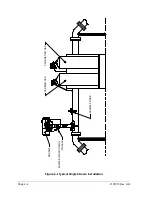
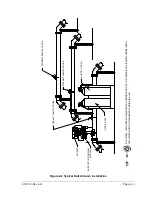
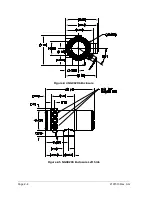
A natural gas sample is extracted from the pipeline, processed for particulate
removal and phase integrity by the sample conditioning module (optional as
required), transported to the NGC and injected onto the chromatographic columns
where component separation occurs.
The NGC analyzes each sample, utilizing established chromatographic
techniques. The resulting information consists of mole percent values for each
component. These values are used to perform energy calculations. Calculated
values include: gas compressibility, real relative density, Btu/CV value, liquid
GPM, Wobbe index, methane number and several other optional calculated
values. Gas compressibility selections include NX-19, AGA-8 detail, single virial
summation factor, ISO summation factor and none (a factor of one is used).
The processed sample is then vented with the carrier gas and results are stored in
memory and communicated to other devices, as needed. All of these values, as
well as composition, are available on various Modbus communication protocols.
2.2.1
Hydrocarbons
To further define the natural gas components,
for each hydrocarbon. Among the key information is the boiling point of the
component. The boiling point of each component correlates to the order each
component will exit the column.
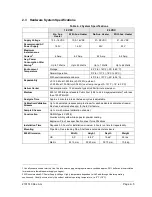
Table 2–1 Hydrocarbons
Molecular
Formula
Common Abbreviation
Component
Boiling Point
C1H4
C1
Methane
-161.60
C2H4
C2=
Ethylene
-103.75
C2H6
C2
Ethane
-88.65
C3H6
C3=
Propylene
-47.65
C3H8
C3
Propane
-42.05
C4H10
IC4
Isobutane
-11.65
C4H8
C4=
Butylene
-6.95
C4H10
C4
Butane
-.45
C5H12
NeoC5
Neopentane
9.85
C5H12
IC5
Isopentane
27.85
C5H12
C5
Pentane
34.85
C6H14
C6
Hexane
68.85
C7H16
C7
Heptane
97.85
C8H18
C8
Octane
125.55
C9H20
C9
Nonane
150.95
C10H22
C10
Decane
173.95