Chapter 8 - Troubleshooting & Maintenance
183
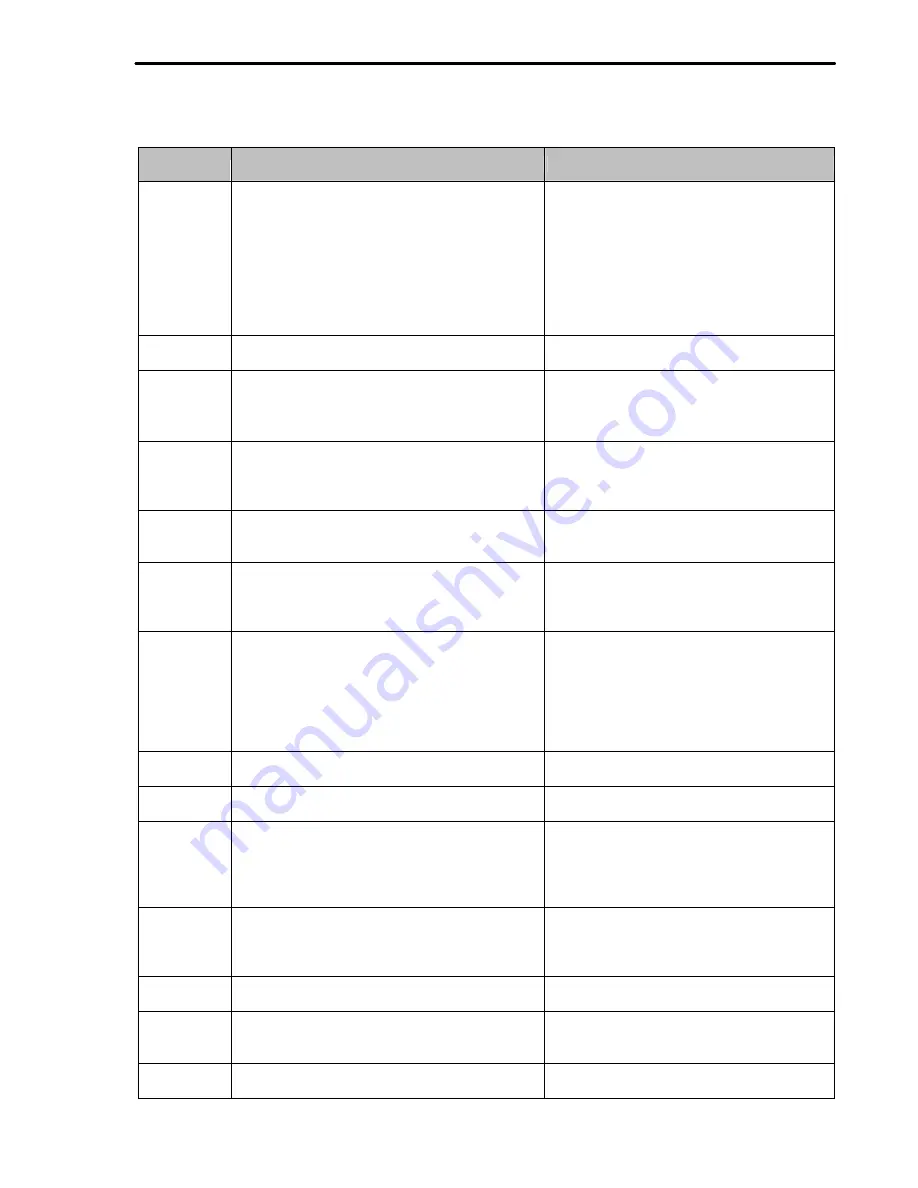
8.2 Fault Remedy
Protective
Function
Cause
Remedy
Over Current
Protection
1) Acceleration/Deceleration time is too short compared to
the GD
²
of the load.
2) Load is larger than the inverter rating.
3) Inverter turns output on when the motor is free running.
4) Output short or ground fault has occurred.
5) Mechanical brake of the motor is operating too fast.
6) Components of the main circuit have overheated due
to a faulty cooling fan.
1) Increase Accel/Decel time.
2) Increase inverter capacity .
3) Operate after motor has stopped.
4) Check output wiring.
5) Check mechanical brake operation.
6) Check cooling fan.
(Caution)
Operating inverter prior to correcting fault
may damage the IGBT.
Ground Current
Protection
1) Ground fault has occurred at the output wiring of inverter.
2) The insulation of the motor is damaged due to heat.
1) Investigate the output wiring of inverter.
2) Exchange motor.
Over Voltage
Protection
1) Acceleration time is too short compared to the GD
²
of
load.
2) Regenerative load at the output
3) Line voltage high
1) Increase deceleration time.
2) Use regenerative resistor option.
3) Check line voltage.
Current Limit
Protection
(Overload
Protection)
1) Load is larger than the inverter rating.
2) Incorrect inverter capacity selected.
3) Set incorrect V/F pattern.
1) Increase capacity of motor and inverter.
2) Select correct inverter capacity .
3) Select correct V/F pattern.
Fuse Damage
1) Damaged due to over use of over current protection.
2) Damaged due to instant deceleration when motor is at an
excessive excitation status.
Exchange the fuse.
(Caution)
The IGBT receives damages on many
occasions when Fuse Open Trip occurs.
Heat Sink
Overheat
1) Cooling fan damaged or an alien substance inserted.
2) Cooling system has faults.
3) Ambient temperature high.
1) Exchange cooling fans and/or eliminate alien
substance.
2) Check for alien substances in the heat sink.
3) Keep ambient temperature under 40
℃
.
Electronic
Thermal
1) Motor has overheated.
2) Load is larger than inverter rating.
3) ETH level too low.
4) Incorrect inverter capacity selected.
5) Set incorrect V/F pattern.
6) Operated too long at low speeds.
1) Reduce load and/or running duty .
2) Increase inverter capacity .
3) Adjust ETH level to an appropriate level.
4) Select correct inverter capacity .
5) Select correct V/F pattern.
6) Install a cooling fan with a separate power supply.
External fault A External fault has occurred.
Eliminate fault at circuit connected to external fault
terminal or cause of external fault input.
External fault B External fault has occurred.
Eliminate fault at circuit connected to external fault
terminal or cause of external fault input.
Low Voltage
Protection
1) Line voltage low.
2) Load larger than line capacity is connected to line.
(welding machine, motor with high starting current
connected to the commercial line)
3) Faulty magnetic switch at the input side of the inverter
1) Check line voltage.
2) Increase line capacity .
3) Exchange magnetic switch.
Over Current 2
1) Short has occurred between the upper and lower IGBT.
2) Short has occurred at the output of the inverter.
3) Acceleration/Deceleration time is too short compared to
the GD
²
of load.
1) Check IGBT.
2) Check output wiring of inverter.
3) Increase acceleration time.
Output Phase
Open
1) Faulty contact of magnetic switch at output
2) Faulty output wiring
1) Check magnetic switch at output of inverter.
2) Check output wiring.
Overspeed
1) Encoder wiring error (A and B wiring switched)
2) Encoder parameter setting is incorrect.
3) Sub-B board or Encoder error
1) Check for the wiring of inverter and encoder
2) Check for parameter setting of EXT-14, 15, and 16.
3) Exchange inverter and encoder for a new one.
H/W Fault
1) Wdog error (CPU fault)
2) EEP error (memory fault)
Exchange inverter.
Morek IT OÜ, Rauna 24, 76506 Saue Harjumaa, Estonia. www.morek.eu Tel. +372 604 1423 Fax +372 604 1447 [email protected]