PID Loop Operation
Maintenance
8–29
PID Loop Operation
IMPORTANT:
The scaling of the SP must be adjusted if you use PV square-root
extract, because the loop drives the output so the
square root
of the PV is equal to
the PV input. Divide the desired SP value by the square root of the analog span, and
use the result in the V+02 location for the SP. This does reduce the resolution of the
SP, but most flow control loops do not require a lot of precision (the recipient of the
flow is integrating the errors). Use one of the following formulas for the SP according
to the data format you are using. It’s a good idea to set the SP upper limit to the top of
the allowed range.
Data Format
SP Scaling
SP Range
PV range
12-bit
SP = PV input / 64
0 – 64
0 – 4095
15-bit
SP = PV input / 181.02
0 – 181
0 – 32767
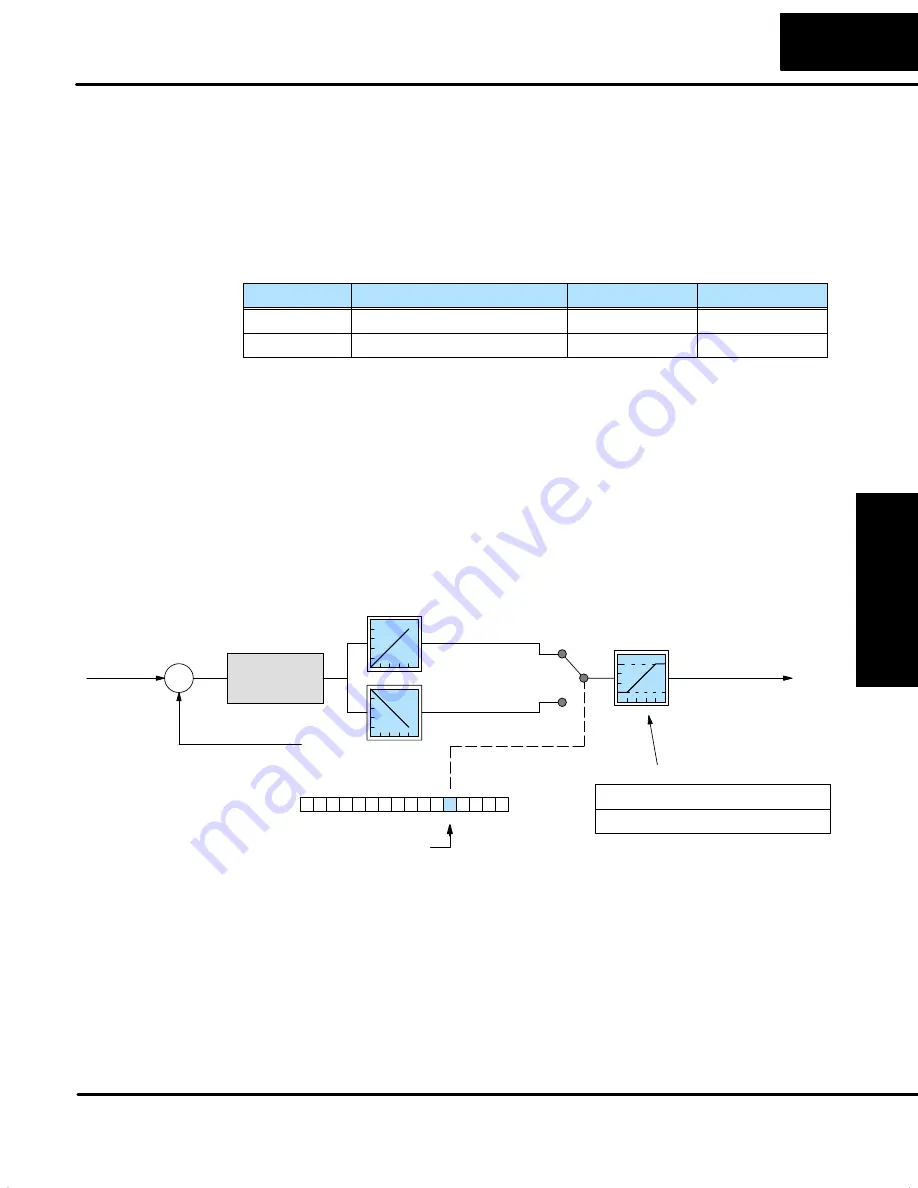
The Control Output is the numerical result of the PID calculation. All of the other
parameter choices ultimately influence the value of a loop’s Control Output for each
calculation. Some final processing selections dedicated to the Control Output are
available, shown below. At the far right of the figure, the final output may be restricted
by lower and upper limits that you program. The values for V+30 and V+31 may be
set once using
Direct
SOFT32’s PID Setup dialog box.
The Control Output lower and upper limits can help guard against commanding an
excessive correction to an error when a loop fault occurs (such as PV sensor signal
loss). However, do not use these limits to restrict mechanical motion that might
otherwise damage a machine (use hard-wired limit switches instead).
Process Variable
Loop
Calculation
S
+
–
Control Output
Setpoint
PID Mode 1 Setting V+00
0
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
Bit
Normal / Inverted Output Select
0
1
Normal Output
Inverted Output
With
Limits
Loop Table
V+30
Control Output Lower Limit
XXXX
V+31
Control Output Upper Limit
XXXX
The other available selection is the normal/inverted output selection (called
“forward/reverse” in
Direct
SOFT). Use bit 4 of the PID Mode 1 Setting V+00 word to
configure the output. Independently of unipolar or bipolar format, a normal output
goes upward on positive errors and downward on negative errors (where
Error=(SP–PV)). The inverted output reverses the direction of the output change.
The normal/inverted output selection is used to configure
direct-acting/reverse-acting loops. This selection is ultimately determined by the
direction of the response of the process variable to a change in the control output in a
particular direction. Refer to the PID Algorithms section for more on direct-acting and
reverse-acting loops.
Control Output
Configuration
Содержание DL05
Страница 1: ...DL05 User Manual Automationdirect com ...
Страница 2: ...DL05 User Manual Automationdirect com ...
Страница 436: ...1B DL05 Error Codes In This Appendix Ċ Error Code Table ...
Страница 443: ...1C Instruction Execution Times In This Appendix Ċ Introduction Ċ Instruction Execution Times ...
Страница 459: ...1D Special Relays In This Appendix Ċ DL05 PLC Special Relays ...
Страница 464: ...1E DL05 Product Weights In This Appendix Ċ Product Weight Table ...
Страница 466: ...1F European Union Directives CE In This Appendix Ċ European Union EU Directives Ċ Basic EMC Installation Guidelines ...
















































