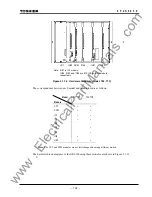
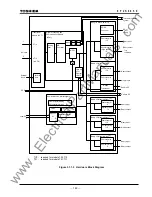
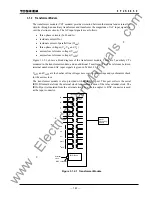
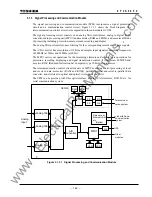
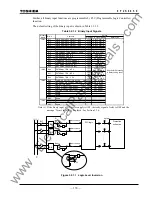
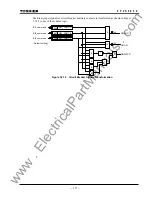
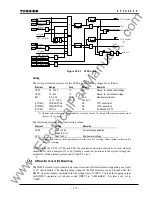
173
6
F
2
S
0
8
5
0
3.3 Automatic
Supervision
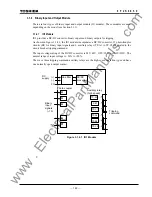
3.3.1 Basic Concept of Supervision
Though the protection system is in the non-operating state under normal conditions, it is waiting
for a power system fault to occur at any time and must operate for faults without fail. Therefore,
the automatic supervision function, which checks the health of the protection system during
normal operation, plays an important role. A numerical relay based on microprocessor
operations is suitable for implementing this automatic supervision function of the protection
system. The GRL100 implements the automatic supervision function taking advantage of this
feature based on the following concept:
•
The supervising function should not affect protection performance.
•
Perform supervision with no omissions whenever possible.
•
When a failure occurs, it should be able to easily identify the location of the failure.
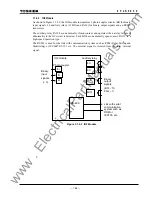
3.3.2 Relay
Monitoring
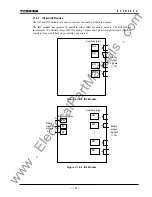
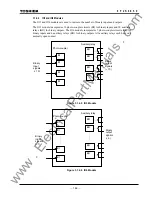
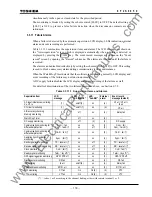
The following items are supervised:
AC input imbalance monitoring
The AC voltage and current inputs are monitored to check that the following equations are
satisfied and the health of the AC input circuits is checked.
•
Zero sequence voltage monitoring
|Va + Vb + Vc| / 3
≤
6.35(V)
•
Negative sequence voltage monitoring
|Va + a
2
Vb + aVc| / 3
≤
6.35(V)
where,
a = Phase shifter of 120
°
•
Zero sequence current monitoring
|Ia + Ib + Ic
−
3Io| / 3
≤
0.1
×
Max(|Ia|, |Ib|, |Ic|) + k0
where,
3Io = Residual current
Max(|Ia|, |Ib|, |Ic|) = Maximum amplitude among Ia, Ib and Ic
k0 = 5% of rated current
These zero sequence monitoring and negative sequence monitoring allow high-sensitivity
detection of failures that have occurred in the AC input circuits.
The negative sequence voltage monitoring allows high sensitivity detection of failures in the
voltage input circuit, and it is effective for detection particularly when cables have been
connected with the incorrect phase sequence.
The zero sequence current monitoring allows high-sensitivity detection of failures irrespective
of the presence of the zero sequence current on the power system by introduction of the residual
circuit current.
Only zero sequence monitoring is carried out for the current input circuit, because zero sequence
www
. ElectricalPartManuals
. com
Summary of Contents for GRL100-701B
Page 329: ... 328 6 F 2 S 0 8 5 0 w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 339: ... 338 6 F 2 S 0 8 5 0 w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 351: ... 350 6 F 2 S 0 8 5 0 w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 381: ... 380 6 F 2 S 0 8 5 0 w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 413: ... 412 6 F 2 S 0 8 5 0 w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 417: ... 416 6 F 2 S 0 8 5 0 w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 453: ... 452 6 F 2 S 0 8 5 0 w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 457: ... 456 6 F 2 S 0 8 5 0 w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 473: ...w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...