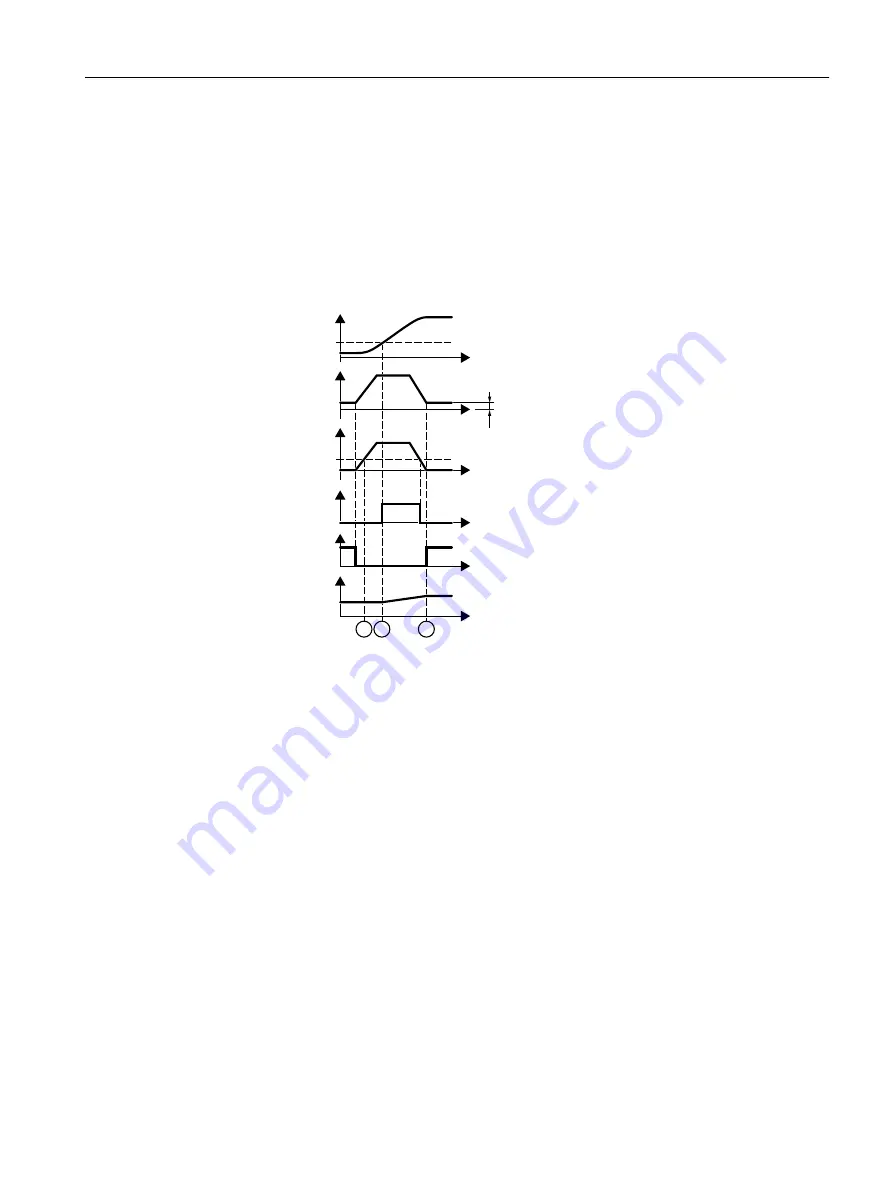
At low speeds, the converter calculates the load torque M
L
from the actual motor torque.
The calculation takes place under the following conditions:
• Speed ≥ p1226
• Acceleration setpoint < 8 1/s
2
(≙ speed change 480 rpm per s)
• Acceleration × moment of inertia (r1493) < 0.9 × p1560
How does the converter calculate the moment of inertia?
0
/
0RPHQWRILQHUWLD
HVWLPDWLRQLVDFWLYH
0RWRUWRUTXH00
0LQLPXPWRUTXH
$FFHOHUDWLQJWRUTXH
0%
6SHHG
/RDGHVWLPDWRULV
DFWLYH
&DOFXODWHGPRPHQWRI
LQHUWLD
U
S
W
W
W
W
W
W
Figure 8-62
Calculating the moment of inertia
For higher speed changes, the converter initially calculates the accelerating torque M
B
as
difference between the motor torque M
M
, load torque M
L
and frictional torque M
R
:
M
B
= M
M
- M
L
- M
R
Moment of inertia J of the motor and load is obtained from the accelerating torque M
B
and
angular acceleration α (α = rate at which the speed changes):
J = M
B
/ α
If all of the following conditions are met, the converter calculates the moment of inertia:
•
①
The rated accelerating torque M
B
must satisfy the following two conditions:
– The sign of M
B
is the same as the direction of the actual acceleration
– M
B
> p1560 × rated motor torque (r0333)
•
②
speed > p1755
• The converter has calculated the load torque in at least one direction of rotation.
• Acceleration setpoint > 8 1/s
2
(≙ speed change 480 rpm per s)
③
The converter calculates the load torque again after acceleration.
Advanced commissioning
8.19 Motor control
Distributed converter for SIMOGEAR geared motors
Operating Instructions, 10/2020, FW V4.7 SP13, A5E31298649B AL
305






























