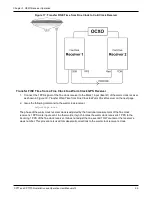
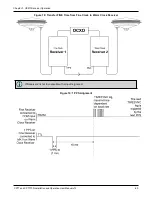
Chapter 3 OEM7 Receiver Operation
CPT7 and CPT7700 Installation and Operation User Manual v12
62
Measuring the RF Input Gain
This section is intended for advanced users.
The
RFINPUTGAIN
command allows users to enter a more accurate receiver input condition, which is
considered as a calibrated receiver input condition, and is used for interference detection. This command
supports different values for L1, L2, L5, and L-Band and is recommended when there is a known strong
interference present at receiver start up.
To calibrate the receiver input level, use a standard spectrum analyzer to measure the receiver input noise
density in dBm/Hz. Make sure the pre-amplifier is turned on in Spectrum Analyzer under “Amplitude”. Place
the Marker around L1, L2, L5, or L-Band frequency region and select “noise density” under “Marker Function”.
RFINPUTGAIN = Receiver Input Noise Density (dBm/Hz) - Typical Thermal Noise KT of -174dBm/Hz,
where:
K = 1.38E-23w-sec/K
T = 290 k.
For example, if the receiver input noise density measured at L1 is -144dBm/Hz,
RFINPUTGAIN = -144 – (-174) = 30dB for L1 path.
Alternatively, if a spectrum analyzer is not available, the RFINPUTGAIN can be obtained using the cascaded
RF gain before the receiver plus LNA noise figure (NF), including LNA gain in antenna, in-line amplifier gain (if
applicable), RF cable or distribution loss prior to receiver input connector. A typical GNSS active antenna with
reasonable quality has a noise figure of ~2dB.
RFINPUTGAIN = Cascaded Gain before re LNA NF
For example, if system cumulative gain measured before receiver is ~25dB, and LNA NF is around 2dB, the
RFINPUTGAIN = 27dB.
RFINPUTGAIN L1 27
RFINPUTGAIN L2 27
RFINPUTGAIN L5 27
RFINPUTGAIN LBand 27
Statistical Analysis Detection
Statistical Analysis Detection is focused on out of band interference detection. It is supplementary to the
Spectrum Analysis Detection and is useful when interference is outside the analog passband of the receiver
and creating distortion that may not be visible to Spectrum Analysis Detection until the interference is very
strong.
The Statistical Analysis Detection is designed as a sensitive detection tool. Out of band mitigation does not
impose much penalty when enabled and it brings awareness to unintentional interferences next to GNSS
operations.
Spectral Analysis Detection takes precedent over Statistical Analysis Detection. If the same
interference is detected by both detectors, only Spectral Analysis Detection is used to report the
interference status.