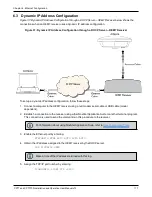
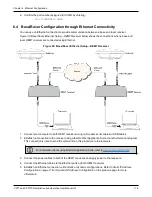
CPT7 and CPT7700 Installation and Operation User Manual v12
122
Chapter 8 CAN Bus
Controller Area Network CAN) is a communication medium which allows for data exchange between devices
using a multi-master serial data communication model. The main advantage of CAN is that multiple devices
can communicate through two inexpensive wires that act as a BUS
The OEM7 receivers support the following CAN protocols:
l
J1939 Transport and Extended Transport Protocol: used for corrections and NovAtel messages (both
transmitting and receiving)
l
NMEA2000: used for standard as well as NovAtel-proprietary messages (transmitting only)
By default, CAN is disabled on OEM7 receivers. Critical CAN configuration parameters such as Parameter
Group Numbers (PGNs), addresses and priorities are system-specific and must be explicitly configured.
The addresses and PGNs are typically allocated when the overall CAN bus topology is determined. A Node
has a unique CAN J1939 NAME and address.
The CPT7 has internal CAN transceivers, however it still requires proper bus terminations.
Refer to
on page 177 for pin-out information.
OEM7 receivers support the following NMEA2000 Parameter Group Messages (PGN) over the CAN bus:
l
PGN 126992 System Time
l
PGN 129025 GNSS Position Rapid Update
l
PGN 129026 COG & SOG Rapid Update
l
PGN 129027 Position Delta High Precision Rapid Update
l
PGN 129029 GNSS Position
l
PGN 129551 GNSS Differential Signal
The following commands and logs are used for CAN configuration:
l
CANCONFIG
command: controls the CAN transceiver hardware and places the receiver
on bus
or
off bus
l
J1939CONFIG
command: assigns the CAN J1939 NAME and address parameters to a Node
l
J1939STATUS
log: reports the status a Node on the J1939 CAN network, such as the claimed address
l
LOG CCOMx PGNabcd
: configures the NMEA2000 messages
l
CCOMCONFIG
command: configures the parameters used by the NovAtel command interface to interact
with the CAN Bus.
CCOM ports with a lower port number have a higher transmission priority.
For information about these commands, see the