Section 8 – Automation Communication Formats
8–9
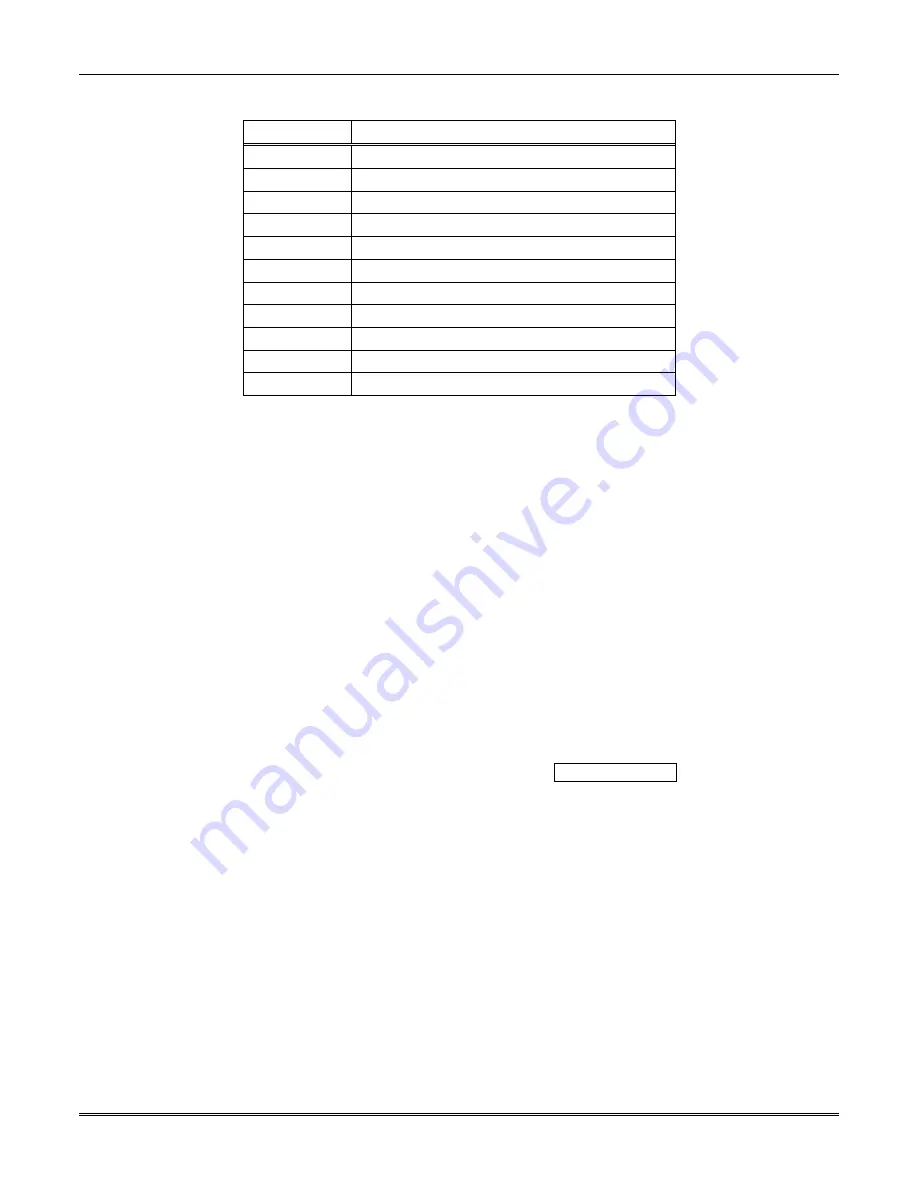
Table 8–12: Link Test Components
Component Description
<$03> Message
type
identifier.
<“051997”>
Date information, consisting of six ASCII bytes.
<$22> Separator
<“074905”>
Time information, consisting of six ASCII bytes
<$22> Separator
<“01”> Receiver
number
<$22> Separator
<“0000”>
Reference number, consisting of four ASCII bytes.
<$22> Separator
<V-byte>
Validation Byte (V-byte). See Section 8.4.5.
<$0D>
End of message indicator.
8.4.5 Validation Byte (V-Byte)
A V-byte always precedes the end of message indicator and is the only error checking used by the ADEMCO
8000 communication format.
The following equations are used to calculate the V-byte:
1. Add the 1st byte of the message to the 2nd byte.
2. Clear bit 7 of the result.
3. Set bit 6 of the result.
4. Add this result to the next byte of the message.
5. Repeat steps 2 through 4 until the last byte of the event data. (Up to and including the byte preceding
the validation byte.) The range of the sum is from $40 to $7F.
8.4.6 ACKing and NACKing Data
After the end of message byte (
<$0D>
) is sent by the receiver, the automation computer will respond with an
ACK (
<$06>
) or NACK (
<$15>
). This response can be delayed between 1 byte time (depending on the baud
rate) and the ACK timeout period. See Section 5.4.3.5 page 5–19.
If the receiver doesn’t get a response within the ACK timeout period or receive a NACK from the automation
computer, it will retransmit the data.
After two NACKs or two ACKs timeout, the receiver will generate a
Computer Trouble
message. When a
computer trouble message is generated, then the receiver will continually send a heartbeat until it receives
an ACK from the automation computer. When communication is restored, a Computer Trouble Restore
message will be generated.
8.4.7 Commands Initiated by the Automation Computer
Typically all communications are initiated by the receiver; however, there are several commands available to
the automation computer to control or request information from the receiver. The automation computer may
send these requests only when the receiver is not transmitting data to it.
The following sub-sections show the message format that must be sent from the automation computer to the
receiver in order that these command requests function properly.
The receiver will respond to these requests from the automation computer with one of the following
messages:
















































