110
Chapter 11 Operation of Debugging Software ()
The following functions can be realized online by using the upper computer software ():
• Parameter management: parameter setting and adjustment
• State monitoring: monitoring the working state and relevant data of the servo system
• Tracking: tracking the servo power supply, command, output current and other related data
• Auxiliary debugging: realize various functions of online auxiliary debugging servo with upper computer
11.1 Connection and login of iWath+ debugging software
1. Install debugging software on PC
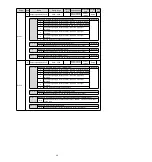
2. The PC is connected to the Mini USB interface on the servo driver panel
operator through a USB connection line. The communication interface is
shown in the right figure.
3. After the communication lines are correctly connected, execute debugging software (icon) on
the PC.
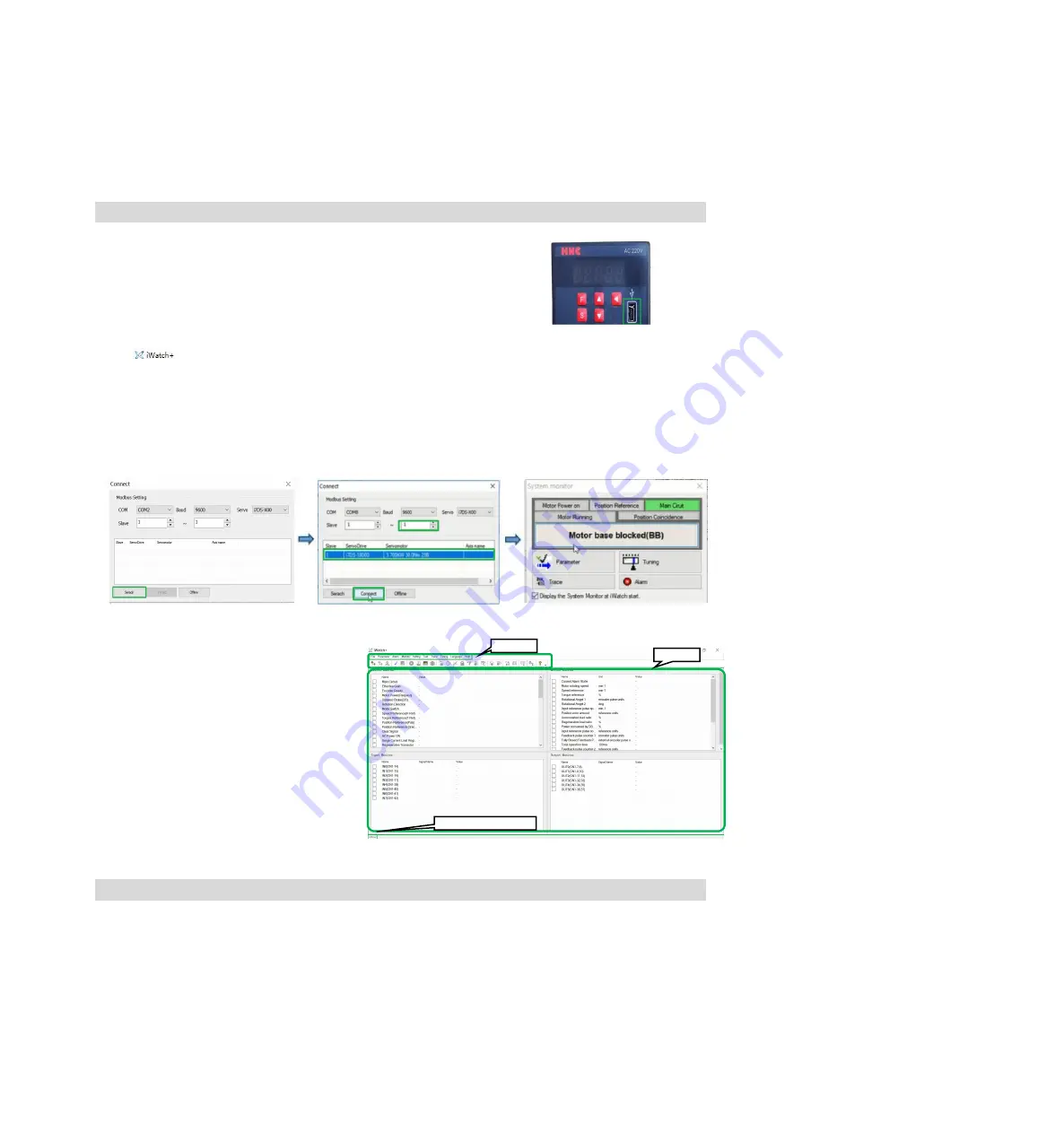
After displaying the [User Login] window, click the [Search] button (Figure 1).
(Two-axis drive selects slave station addresses 1 ~ 2, and the searched address 1 is the drive A axis and
address 2 is the drive B axis)
4. After the [Connect] window is displayed, select the searched drive address 1 or address 2, and then click
the [Connect] button (Figure 2).
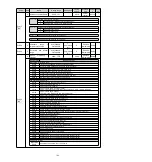
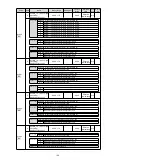
5. The [system monitoring] shortcut window (Figure 3) and the [] debugging window (Figure 4) will be
displayed after successful connection.
Figure 1
Figure 2
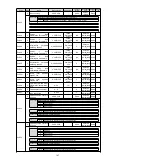
Figure 3
At this time, debugging software is
successfully connected.
In the [] debugging window, various
states of servo can be selectively monitored
in each window.
In the menu bar of the [] debugging
window, you can click the shortcut button for
debugging to enter the debugging interface.
11.2 Automatic adjustment (no upper command)
Automatic adjustment (no upper command) refers to the function that the servo unit performs automatic
operation (reciprocating motion of forward rotation and reverse rotation) without issuing a command from the
upper device and adjusts according to mechanical characteristics during operation.
The automatic adjustment items are as follows.
• Moment of inertia ratio
• Gain adjustment (speed loop gain, position loop gain, etc.)
• Filter adjustment (torque command filter, notch filter)
• Friction compensation
• Type A vibration suppression control
• Vibration abatement
Communication status
Shortcut
menu bar
Monitoring
window