7
-2
Protective and Diagnostic Functions
This section describes the alarm functions of the Inverter. The alarm functions include fault detection,
alarm detection, operation error detection, and autotuning error detection.
Fault Detection
When the Inverter detects a fault, the fault contact output operates, and the Inverter output is shut OFF causing
the motor to coast to a stop. (The stopping method can be selected for some faults, and the selected stopping
method will be used with these faults.) A fault code is displayed on the Digital Operator.
When a fault has occurred, refer to the following table to identify and correct the cause of the fault.
Be sure to turn Run Command to OFF first, use one of the following methods to reset the fault before restart-
ing the Inverter.
•
Set a multi-function contact input (H1-01 to H1-06) to 14 (Fault Reset) and turn ON the fault reset signal.
•
Press the RESET Key on the Digital Operator.
•
Turn the main circuit power supply OFF and then ON again.
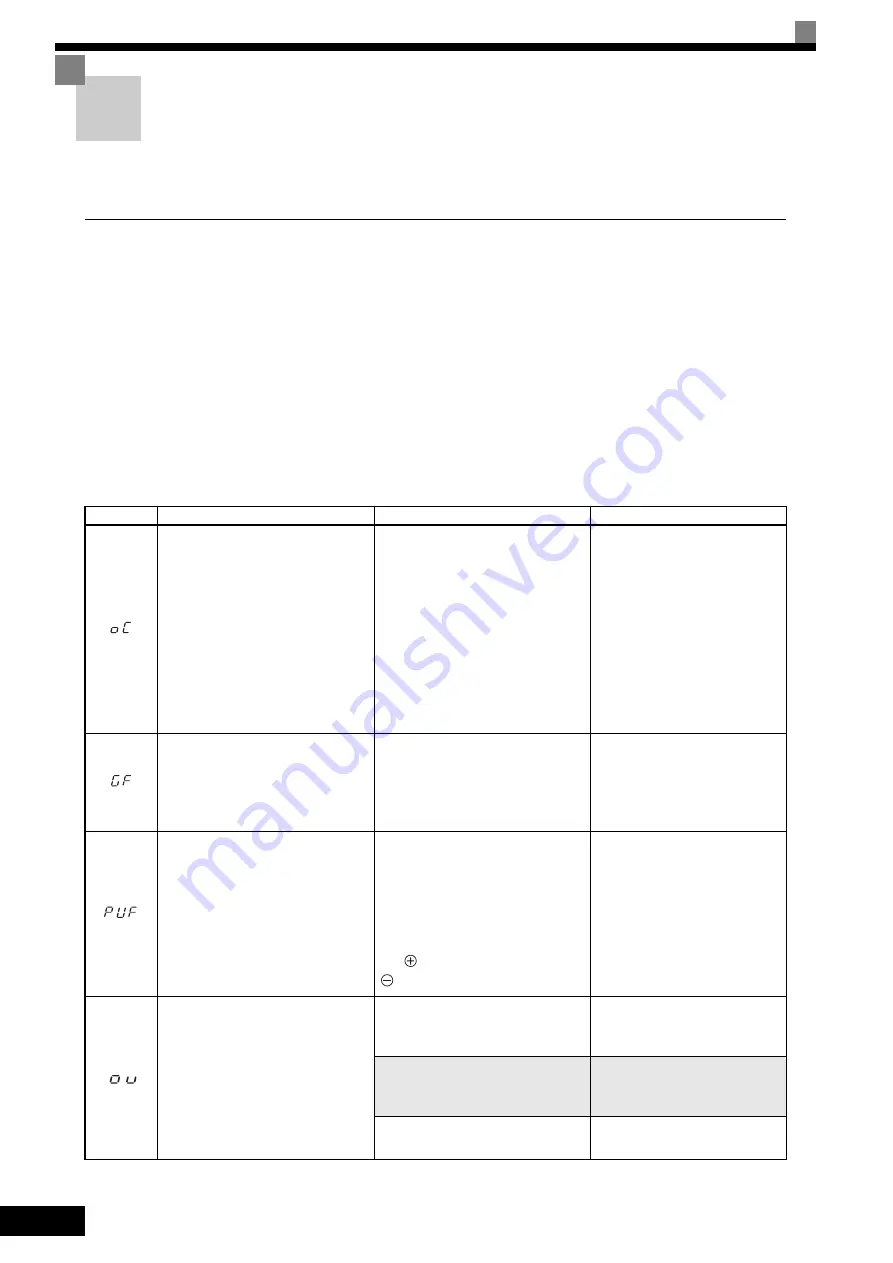
Table 7.1 Fault Displays and Processing
Display
Meaning
Probable Causes
Corrective Actions
Overcurrent
The Inverter output current exceeded
the overcurrent detection level. (200%
of rated current)
• A short-circuit or ground fault
occurred at the Inverter output. (A
short or ground fault can be caused
by motor burn damage, worn insu-
lation, or a damaged cable.)
• The load is too large or the accelera-
tion/deceleration time is too short.
• A special-purpose motor or motor
with a capacity too large for the
Inverter is being used.
• A magnetic switch was switched at
the Inverter output.
Reset the fault after correcting its
cause.
Ground Fault
*
The ground fault current at the
Inverter output exceeded approxi-
mately 50% of the Inverter rated out-
put current.
A ground fault occurred at the Inverter
output. (A ground fault can be caused
by motor burn damage, worn insula-
tion, or a damaged cable.)
Reset the fault after correcting its
cause.
Fuse Blown
The fuse in the main circuit is blown.
The output transistor has failed
because of a short-circuit or ground
fault at the Inverter output.
Check whether there is a short-circuit
between the following terminals. A
short-circuit will damage the output
transistor:
B1 (
3)
←→
U, V, W
←→
U, V, W
Replace the Inverter after correct-
ing the cause.
Main Circuit Overvoltage
The main circuit DC voltage exceeded
the overvoltage detection level.
200 V Class: Approx. 410 V
400 V Class: Approx. 820 V
The deceleration time is too short and
the regenerative energy from the
motor is too large.
Increase the deceleration time or
connect a braking resistor (or
Braking Resistor Unit).
The regenerative energy when an
overshoot occurs after acceleration is
completed is too large.
In vector control, enable (Set to 1)
the overvoltage inhibit selection
(L3-11).
The power supply voltage is too high.
Decrease the voltage so it's within
specifications.
* The ground fault here is one which occurs in the motor wiring. A ground fault with low resistance which occurs in motor cables or terminals may not be detected.
















































