14
BACnet
4.0
BACnet
BACnet stands for Building Automation and Control NETworks (
http://www.bacnet.org)
. It is
an object-oriented communications protocol designed to consolidate different building
regulation systems to allow for collective monitoring and control through a single application.
Building regulation systems that can support the BACnet standard include heating, ventilation,
lighting control, access control as well as fire detection and alarm systems.
The Flex-Net system is capable of interfacing with other systems that communicate through
BACnet to provide centralized control and monitoring of a building’s regulation systems. The
BACnet protocol works by adapting different communication systems into a common
communication format.
The consolidation of different communication systems is accomplished through the use of
“objects”. An object is defined as a collection of information related to a particular function that
can be uniquely identified and accessed over a network in a standardized way. The BACnet
protocol represents all information using these object data structures. Each object is defined
by a set of properties.
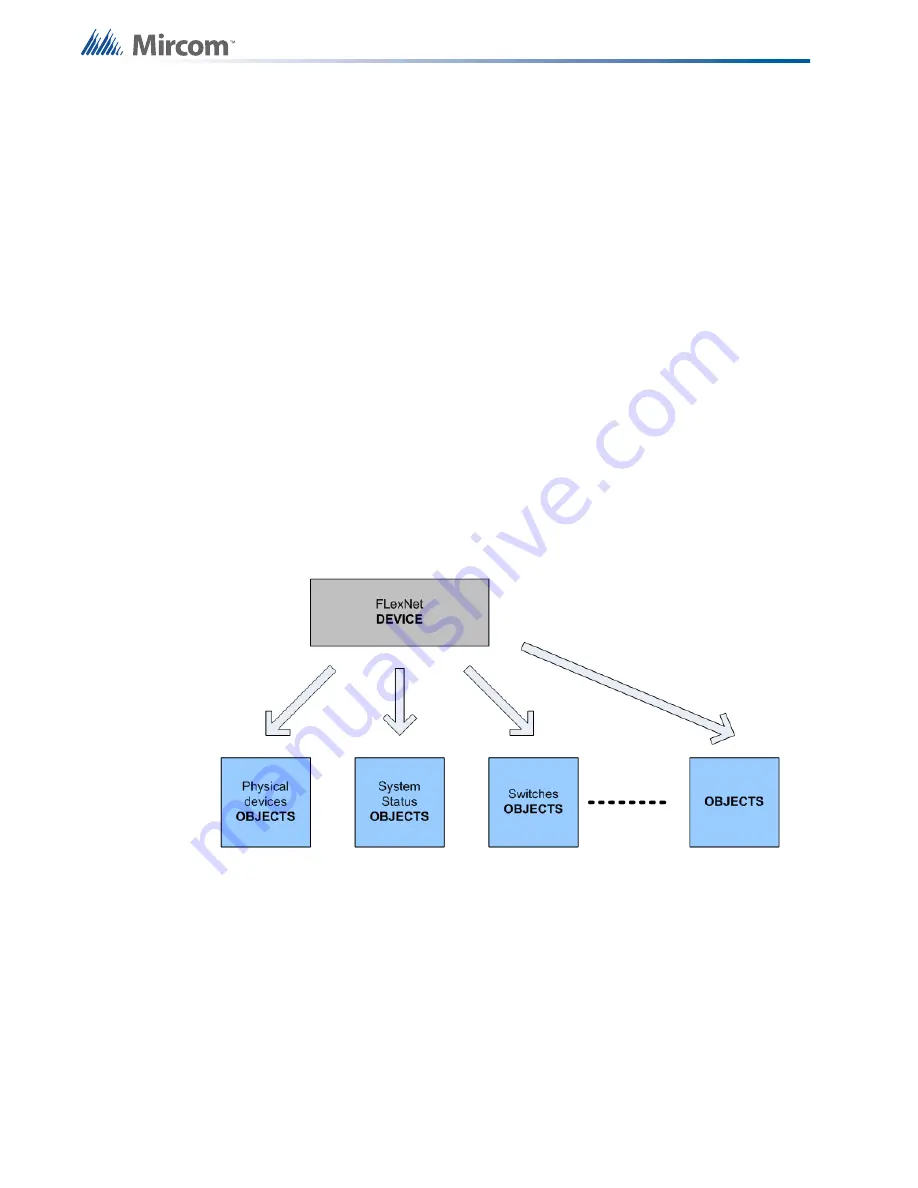
A confusion of terminology may arise when describing Flex-Net under the BACnet model.
Traditionally in the fire alarm industry the term “device” refers to things such as detectors,
strobes and alarms. For BACnet implementation, the entire Flex-Net system is modeled as a
“device” with many “objects”. The term “objects” refers to all the fire devices, system statuses
and switches connected to the Flex-Net system. This is illustrated in the figure below.
Objects are all assigned properties that help define them and allow them to be monitored and
controlled. Objects can be classified into one of several different types. For example fire
devices can be subdivided into categories such as binary inputs, binary outputs, analog inputs
and analog outputs. In addition to an object type every object must be assigned an object
identifier and an object name. Depending on the type of BACnet device that the object is
associated with there will be more required properties that need to be assigned and others
that are optional.
BACnet uses a peer to peer architecture where any device can send service requests to any
other device. Protocol services include Who-Is, I-Am, Who-Has and I-Have for the purpose of
BACnet device and object discovery. These discovery service requests can be performed by
any BACnet device or object. BACnet services can provide event notifications such as
troubles or input activations. The services can also request current values from the Flex-Net
system.
Summary of Contents for Flex-Net Phase II
Page 1: ...Flex Net Phase II Application Guide LT 6045 Rev 1 October 2012 Application Guide...
Page 2: ......
Page 51: ...51 Hardware Layouts...
Page 115: ...114 Appendix B Using the Configurator...
Page 131: ......















































