Goodrive20-UL Series VFD
Communication protocol
-117-
renew the uncompleted message and suppose the next byte as the address field of the new
message. As such, if the new message follows the previous one within the interval time of 3.5
bytes, the receiving device will deal with it as the same with the previous message. If these
two phenomena all happen during the transmission, the CRC will generate a fault message to
respond to the sending devices.
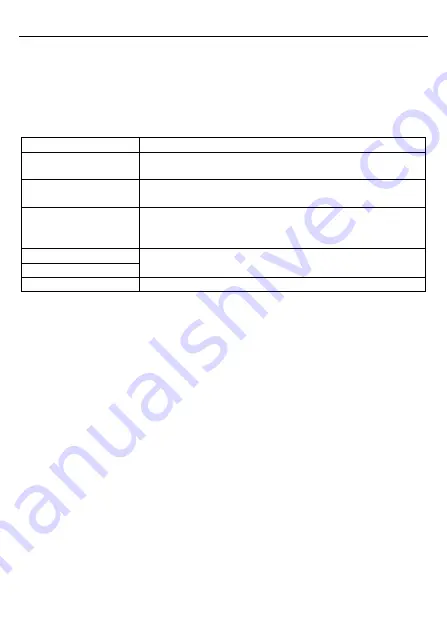
The standard structure of RTU frame:
START
T1-T2-T3-T4 (transmission time of 3.5 bytes)
ADDR
Communication address: 0
–247 (decimal system) (0 is the
broadcast address)
CMD
03H: read slave parameters
06H: write slave parameters
DATA (N-1)
…
DATA (0)
The data of 2 x N bytes are the main content of the
communication as well as the core of data exchanging
CRC CHK low bit
Detection value: CRC (16 BIT)
CRC CHK high bit
END
T1-T2-T3-T4 (transmission time of 3.5 bytes)
7.2.2.2 RTU communication frame error check modes
Various factors (such as electromagnetic interference) may cause error in the data
transmission. For example, if the sending message is logic "1", A-B potential difference on
RS485 should be 6V, but in reality, it may be -6V because of electromagnetic interference, and
then the other devices take the sent message as logic "0". If there is no error checkout, the
receiving devices will not find the message is wrong and they may give incorrect response
which cause serious result. So the checkout is essential to the message.
The theme of checkout is that: the sender calculate the sending data according to a fixed
formula, and then send the result with the message. When the receiver gets this message,
they will calculate anther result according to the same method and compare it with the sending
one. If two results are the same, the message is correct. If not, the message is incorrect.
The error checkout of the frame can be divided into two parts: the bit checkout of the byte and
the whole data checkout of the frame (CRC check).
Bit check on individual bytes (odd/even check)
The user can select different bit checkouts or non-checkout, which impacts the check bit
setting of each byte.
The definition of even checkout: add an even check bit before the data transmission to
illustrate the number of "1" in the data transmission is odd number or even number. When it is
even, the check byte is "0", otherwise, the check byte is "1". This method is used to stabilize
Summary of Contents for GD20-0R4G-2-UL
Page 1: ......
















































