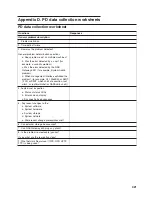
electromagnetic compatibility (EMC).
The design
and test of products to meet legal and corporate
specifications dealing with the emissions and
susceptibility to frequencies in the radio spectrum.
Electromagnetic compatibility is the ability of various
electronic equipment to operate correctly in the intended
electromagnetic environment.
Electronic Industries Association (EIA).
An
organization of electronics manufacturers that advances
the technological growth of the industry, represents the
views of its members, and develops industry standards.
Electronic Industries Association (EIA) unit.
A unit
of measure equal to 4.45 cm (1.75 in.).
electrostatic discharge (ESD).
An undesirable
discharge of static electricity that can damage
equipment and degrade electrical circuitry.
EMC.
See
electromagnetic compatibility
.
engine.
The unit that contains the processors that
respond to requests for data from clients. The operating
software for the NAS Gateway 500 resides in the
engine.
equivalent paths.
A collection of paths to the storage
device. The paths have no switchover time penalty
when changing from one path group to another while
accessing the storage device.
error.
A discrepancy between a computed, observed,
or measured value or condition and the true, specified,
or theoretically correct value or condition (A) (I).
Contrast with
failure
.
ESD.
See
electrostatic discharge
.
ESM.
See
environmental service monitor
.
Ethernet.
A standard protocol for a 10-Mbps baseband
local area network (LAN) that allows multiple access
and manages contention by using carrier sense multiple
access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) as the
access method.
Ethernet network.
A baseband LAN with a bus
topology in which messages are broadcast on a coaxial
cable using a carrier sense multiple access/collision
detection (CSMA/CD) transmission method.
expansion slot.
In personal-computer systems, one of
several receptacles in the rear panel of the system unit
into which a user can install an adapter.
Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA).
The PC bus standard that extends the AT bus (ISA bus)
to 32 bits and provides support for bus master. It was
announced in 1988 as a 32-bit alternative to the Micro
Channel that would preserve investment in existing
boards. PC and AT cards (ISA cards) can plug into an
EISA bus.
F
fabric.
A complex network using hubs, switches and
gateways. For example, Fibre Channel uses a fabric to
connect devices. A fabric can be as simple as a single
cable connecting two devices.
failback.
The restoration of the NAS Gateway 500 to
its initial configuration after detection and repair of a
failed network or component.
failover.
(1) The automatic recovery of resources in
the event of a network outage, or failure of the
hardware or software. (2) A cluster event in which the
primary database server or application server switches
to a backup system due to the failure of the primary
server.
failure.
(1) The termination of the ability of a functional
unit to perform its required function. (2) An uncorrected
hardware error. Failures are either recoverable or not
recoverable by the software or the operator. The
operator is always notified when failures occur. Contrast
with
error
.
fallover.
Also called failover. The process of an active
node acquiring resources previously owned by another
node, in order to maintain availability of those
resources.
fallback.
Also called failback. Process of a joining or
reintegrating node acquiring resources previously owned
by another node.
Fast Etherchannel (FEC).
A proprietary technology
developed by Cisco that creates a team of two to four
10/100 Ethernet adapters or ports to increase
transmission and reception throughput. Adapter fault
tolerance is also supported by this technology.
Fast Ethernet.
An Ethernet standard that provides a
data rate of 100 Mbps.
feature code.
A code used by IBM to process
hardware and software orders.
FEC.
See
Fast Etherchannel
.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
A
board of commissioners appointed by the President
under the Communications Act of 1934, having the
power to regulate all interstate and foreign
communications by wire and radio originating in the
United States.
fiber optic cable.
See
optical cable
.
field-replaceable unit (FRU).
An assembly that is
replaced in its entirety when any one of its components
fails. In some cases, a FRU may contain other FRUs.
Contrast with
customer-replaceable unit
.
Glossary
435
Summary of Contents for TotalStorage NAS Gateway 500
Page 1: ...IBM TotalStorage NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide GY27 0418 00 ...
Page 2: ......
Page 3: ...IBM TotalStorage NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide GY27 0418 00 ...
Page 16: ...xiv NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 20: ...xviii NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 36: ...System logic flow Note Not all components are supported 16 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 52: ...32 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 58: ...38 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 112: ...92 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 266: ...246 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 326: ...306 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 353: ...Chapter 11 Removal and replacement procedures 333 ...
Page 392: ...372 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 402: ...382 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 412: ...392 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 440: ...420 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 446: ...426 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 448: ...428 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 466: ...446 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide ...
Page 469: ......
Page 470: ... Printed in U S A GY27 0418 00 ...
Page 471: ...Spine information IBM TotalStorage NAS Gateway 500 NAS Gateway 500 Service Guide GY27 0418 00 ...