VLT
®
8000 AQUA
■
Air humidity
VLT 8000 AQUA has been designed to meet the
IEC 68-2-3 standard, EN 50178 pkt. 9.4.2.2/DIN
40040, class E, at 40°C.
See specifications under
General technical data.
■
Efficiency
To reduce energy consumption it is very important
to optimize the efficiency of a system. The
efficiency of each single element in the system
should be as high as possible.
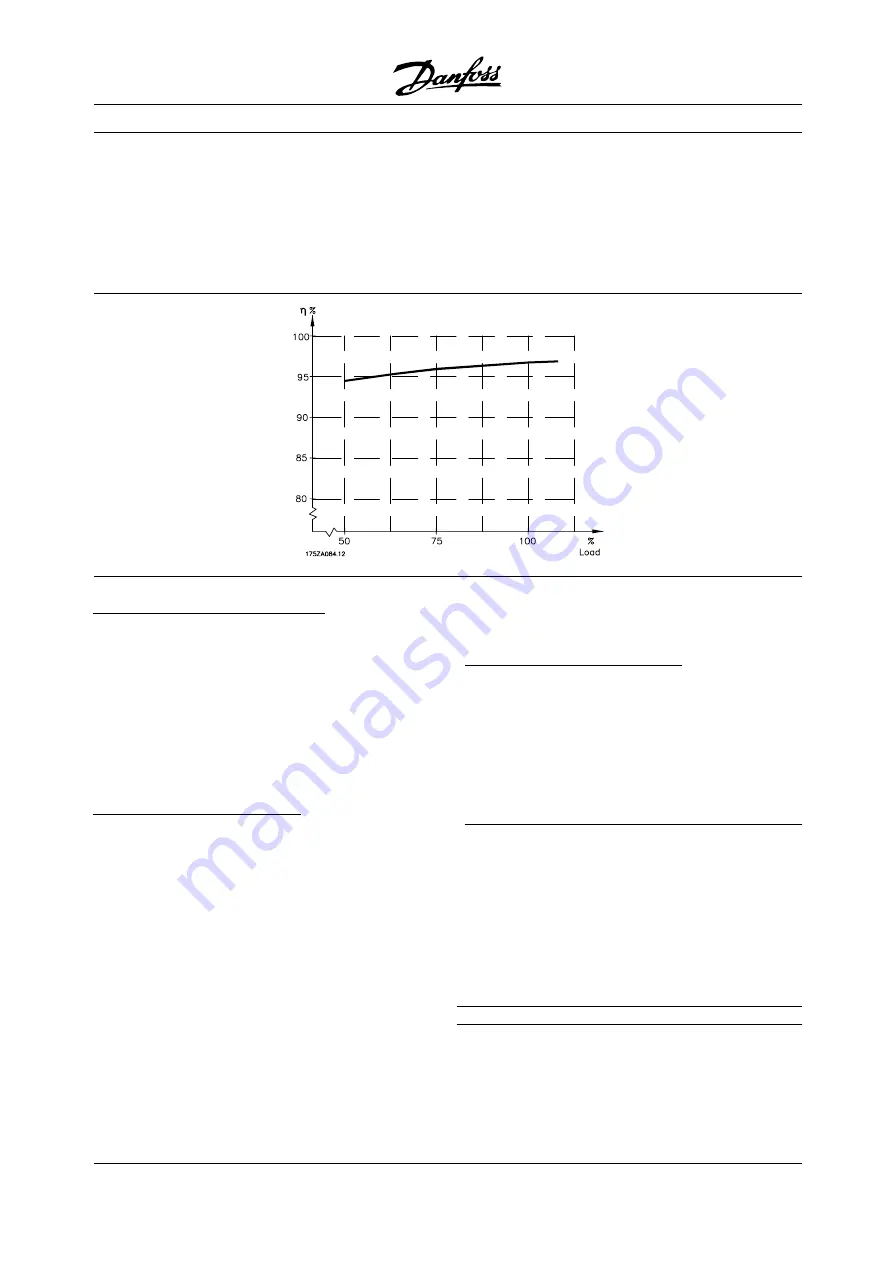
Efficiency of VLT 8000 AQUA (
η
VLT
)
The load on the AFD has little effect on its efficiency.
In general, the efficiency is the same at the rated
motor frequency f
M,N
, regardless of whether the
motor supplies 100% of the rated shaft torque or
only 75%, i.e. in case of part loads.
The efficiency declines a little when the switching
frequency is set to a value of above 4 kHz
(parameter 407
Switching frequency
).
Efficiency of the motor (
η
MOTOR
)
The efficiency of a motorconnected to the AFD
depends on the sine shape of the current. In general,
the efficiency is just as good as with line operation. The
efficiency of the motor depends on the type of motor.
In the range of 75-100% of the rated torque,
the efficiency of the motor is practically constant,
both when it is controlled by the AFD and
when it runs directly on line.
In small motors, the influence from the U/f characteristic
on efficiency is marginal; however, in motors from 15
HP and up, the advantages are significant.
In general, the switching frequency does not affect
the efficiency of small motors. Motors from 15 HP
and up have their efficiency improved (1-2%). This
is because the sine shape of the motor current is
almost perfect at high switching frequency.
Efficiency of the system (
η
SYSTEM
)
To calculate the system efficiency, the efficiency
of VLT 8000 AQUA (VLT) is multiplied by the
efficiency of the motor (
η
MOTOR
):
η
SYSTEM
=
η
VLT
x
η
MOTOR
Based on the graph outlined above, it is possible to
calculate the system efficiency at different speeds.
■
Line supply interference/harmonics
An AFD takes up a non-sinusoidal current from
line, which increases the input current I
RMS
. A
non-sinusoidal current can be transformed by means
of a Fourier analysis and split up into sine wave currents
with different frequencies, i.e. different harmonic
currents I
N
with 50 Hz as the basic frequency:
Harmonic currents
I
1
I
5
I
7
Hz
50 Hz
250 Hz
350 Hz
The harmonics do not affect the power consumption
directly, but increase the heat losses in the installation
(transformer, cables). Consequently, in plants
with a rather high percentage of rectifier load,
MG.80.A7.22 - VLT is a registered Danfoss trademark
184
Rosewood STP ST42 General (Operation and Maintenance Manual - Part 4:
Section 6.3 Manufacturers Manuals 6.3.33 Danfoss VLT Aquadrive 8000) Vendor Manual
QP Id: VM207
Active: 03/09/2013
Page 190 of 208