3 Product Description
C-863.12 Mercury Controller
MS249E
Version: 1.2.1
21
3.5.9
Servo Algorithm and Other Control Value Corrections
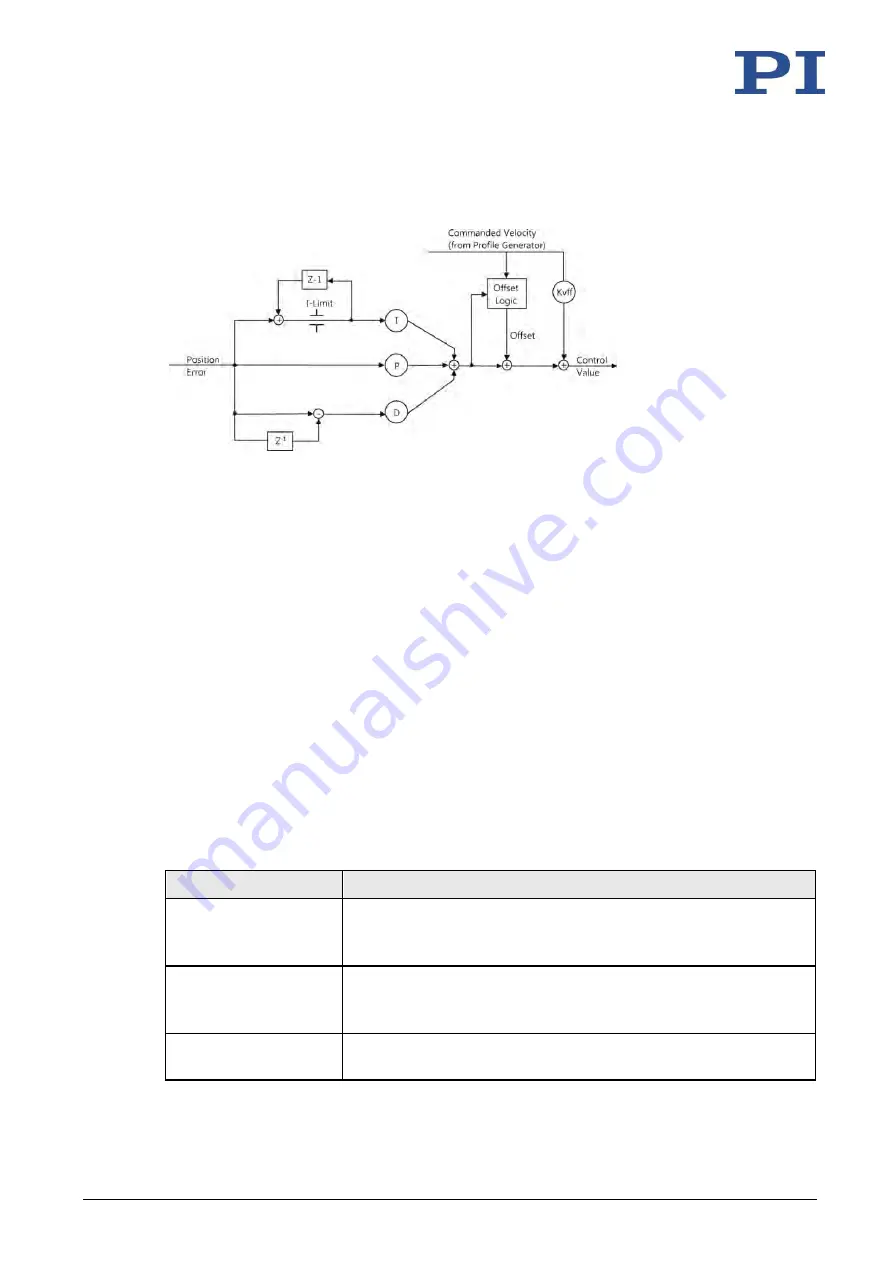
Figure 7: PID algorithm, offset correction and feed-forward control of the velocity (KVff); the notch filter
is not shown here
In closed-loop operation, the control value for the PWM converter integrated in the C-863.12
and therefore the settling behavior of the system is optimized via the following corrections:
▪
Servo algorithm: The position error, which results from the difference between the
calculated dynamics profile (see "Generation of Dynamics Profile" (p. 18)) and the
actual position (sensor feedback), runs through a PID servo algorithm (
p
roportional
i
ntegral
d
erivative).
▪
Dynamics profile corrections: The dynamics profile generated can be subject to an
offset correction and a feed-forward control of the velocity.
Regardless of the operating mode, the control value can be subjected to an additional
correction via the notch filter.
Servo algorithm
The servo algorithm uses the following servo control parameters. The optimum servo control
parameter setting depends on your application and your requirements; see "Optimizing Servo
Control Parameters" (p. 66).
Parameters
Description and Possible Values
P Term
0x411
Proportional constant (dimensionless)
0 to 32767
Aim: Rapid correction of the position error
I Term
0x412
Integration constant (dimensionless)
0 to 32767
Objective: Reduction of static position error
D Term
0x413
Differential constant (dimensionless)
0 to 32767






























