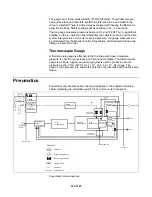
power board are at their proper levels, and that there are no faults. During normal
operation, all green LEDs should be on.
The power board supplies most of the regulated voltages for other electronic
subsystems in the spectrometer. The voltages i5 volts for digital
components, ±15 volts for analog components (such as amplifiers), +24 volts for
all the heaters except the manifold, 60 volts for the trapping field RF generator.
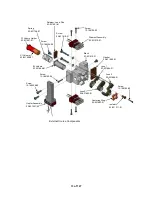
Manifold Electronics
The manifold electronics consists of two boards stacked in an enclosure directly
on top of the vacuum manifold. The boards perform a variety of functions related
to the ionization and mass scanning processes. Functions related to the external
source include providing lens voltages and heater control. These boards provide
filament control for both external and internal ionization.
The function of the upper manifold board is to handle the signals that are applied
to the ion trap end cap electrodes. As explained in the user guides, dipole
waveforms are applied to the end caps during the ionization, isolation and mass
scanning processes. Quadrupole waveforms are applied during the mass
scanning process. The dipole signal is applied, out of phase, to the two end caps
to provide a signal across the end caps. The quadrupole is applied in phase to
provide a voltage between the end caps and the ring electrode. Waveform
signals are received from the controller board through the power board. They are
then buffered by high-power operational amplifiers and applied to the end caps
through transformers that step up the waveform voltage. Two transformers apply
the dipole waveforms, one for high frequency dipole waveforms and the other for
low frequency square waves applied during non resonant CID. A trapping field
dipole (TFD) voltage is applied during the mass scanning process to offset the
trapped ions from the center of the trap. The TFD signal is derived from trapping
field RF currents flowing in the end caps coupled from the 1 MHz signal applied
to the ring electrode by the RF generator and coil. The TFD is switched on and
off by changing the impedance between end caps and ground; when the TFD is
off, a low impedance is switched in. When the TFD is turned on, a high capacitive
impedance on one end cap and inductance impedance on the other end cap are
switched on, resulting in the out of phase dipole signal.
The lower manifold board handles a number of source related electronics
functions. It has amplifiers that apply the appropriate lens voltages to the source,
based on set points received from the controller board. The source filament
emission regulator circuit is also present on the board. In addition, there is also
conditioning electronics that produce high-level temperature measurement
signals from resistive temperature devices (RTDs) on the source and traps that
are used for temperature control and diagnostic purposes.
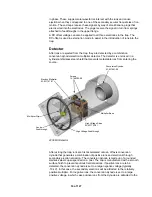
RF Generator Assembly
The RF generator assembly consists of an RF generator circuit board, an RF
detector circuit board, and the RF coil. A shielded housing beneath the vacuum
manifold encloses the coil and RF detector circuit board. The RF generator circuit
board is attached to the back of the shielded housing.
The RF generator circuit board receives an analog signal from the controller
board that is proportional to the current mass position in the scan, which is in turn
proportional to the desired RF voltage applied to the ion trap. The RF detector
circuit board sends a signal proportional to the actual amount of RF voltage
applied to the ion trap to the RF generator board. The RF generator board
24 of 127
Summary of Contents for 4000 GC
Page 4: ......
Page 40: ...6 of 127...
Page 77: ...3 Check source connection pins for proper alignment and straighten as necessary 43 of 127...
Page 124: ...90 of 127...
Page 148: ...114 of 127...