in phase. These supplemental waveforms interact with the ions and cause
ejection when they correspond to one of the secondary secular frequencies of ion
motion. The end caps receive these signals by way of small banana plugs that
are inserted into the electrodes. The plugs receive the signal in turn from springs
attached to feedthroughs in the upper flange.
A DC offset voltage can also be applied to all three electrodes in the trap. The
DC offset is used in external ion mode to assist in the introduction of ions into the
trap.
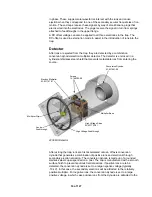
Detector
After ions are ejected from the trap, they are detected by a combination
conversion dynode/electron multiplier detector. The detector is enclosed in a
cylindrical stainless steel shield that prevents metastable ions from entering the
source.
High Voltage Strap
03-931753-01
Multiplier Base
Electron Multiplier
03-931751-01
Screws
12-168304-00
Conversion Dynode
03-931691-00
Multiplier Clip
Anode
Feedthrough
High Voltage Feedthrough
4000 MS Detector
After exiting the trap, ions are first accelerated onto an off axis conversion
dynode that generates a combination of positive ions and electrons through
secondary electron emission. The conversion dynode is made up of a rounded
stainless steel cup suspended on a post. The cup is manufactured with a smooth
surface finish to prevent spurious field emissions. If positive ions are to be
detected, the conversion dynode is set to a large negative voltage (typically
-10 kV). In this case, the secondary electrons will be attracted to the relatively
positive multiplier. For negative ions, the conversion dynode is set to a large
positive voltage, in which case positive ions from the dynode are attracted to the
16 of 127
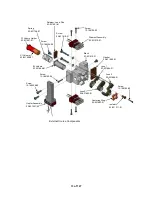
Summary of Contents for 4000 GC
Page 4: ......
Page 40: ...6 of 127...
Page 77: ...3 Check source connection pins for proper alignment and straighten as necessary 43 of 127...
Page 124: ...90 of 127...
Page 148: ...114 of 127...