Firmware Design
P746/EN FD/G31
MiCOM P746
(FD) 9-
19
FD
4.
SELF TESTING & DIAGNOSTICS
The relay includes a number of self-monitoring functions to check the operation of its
hardware and software when it is in service. These are included so that if an error or fault
occurs within the relay’s hardware or software, the relay is able to detect and report the
problem and attempt to resolve it by performing a re-boot. This involves the relay being out
of service for a short period of time which is indicated by the ‘Healthy’ LED on the front of the
relay being extinguished and the watchdog contact at the rear operating. If the restart fails to
resolve the problem, then the relay will take itself permanently out of service. Again this will
be indicated by the LED and watchdog contact.
If a problem is detected by the self-monitoring functions, the relay attempts to store a
maintenance record in battery backed-up SRAM to allow the nature of the problem to be
notified to the user.
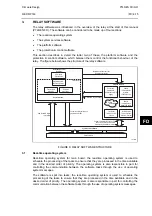
The self-monitoring is implemented in two stages: firstly a thorough diagnostic check which
is performed when the relay is booted-up, e.g. at power-on, and secondly a continuous self-
checking operation which checks the operation of the relay’s critical functions whilst it is in
service.
4.1 Start-up
self-testing
The self-testing which is carried out when the relay is started takes a few seconds to
complete, during which time the relay’s protection is unavailable. This is signalled by the
‘Healthy’ LED on the front of the relay which will illuminate when the relay has passed all of
the tests and entered operation. If the testing detects a problem, the relay will remain out of
service until it is manually restored to working order.
The operations that are performed at start-up are as follows:
4.1.1 System
boot
The integrity of the flash memory is verified using a checksum before the program code and
data stored in it is copied into SRAM to be used for execution by the processor. When the
copy has been completed the data then held in SRAM is compared to that in the flash to
ensure that the two are the same and that no errors have occurred in the transfer of data
from flash to SRAM. The entry point of the software code in SRAM is then called which is the
relay initialization code.
4.1.2 Initialization
software
The initialization process includes the operations of initializing the processor registers and
interrupts, starting the watchdog timers (used by the hardware to determine whether the
software is still running), starting the real-time operating system and creating and starting the
supervisor task. In the course of the initialization process the relay checks:
•
The status of the battery
•
The integrity of the battery backed-up SRAM that is used to store event, fault and
disturbance records
•
The voltage level of the field voltage supply which is used to drive the opto-isolated
inputs
•
The operation of the LCD controller
•
The watchdog operation
At the conclusion of the initialization software the supervisor task begins the process of
starting the platform software.
Summary of Contents for MiCOM P746
Page 4: ......
Page 5: ...Pxxx EN SS G11 SAFETY SECTION...
Page 6: ......
Page 8: ...Pxxx EN SS G11 Page 2 8 Safety Section BLANK PAGE...
Page 16: ...P746 EN IT G31 Introduction MiCOM P746...
Page 18: ...P746 EN IT G31 Introduction IT 1 2 MiCOM P746 IT BLANK PAGE...
Page 26: ...P746 EN TD G31 Technical Data MiCOM P746...
Page 38: ...P746 EN GS G31 Getting Started MiCOM P746...
Page 78: ...P746 EN ST G31 Getting Started MiCOM P746...
Page 80: ...P746 EN ST G31 Settings ST 4 2 MiCOM P746 ST BLANK PAGE...
Page 112: ...P746 EN ST G31 Settings ST 4 34 MiCOM P746 ST BLANK PAGE...
Page 114: ...P746 EN OP G31 Operation MiCOM P746...
Page 136: ...P746 EN OP G31 Operation OP 5 22 MiCOM P746 OP BLANK PAGE...
Page 138: ...P746 EN AP G31 Application Notes MiCOM P746...
Page 142: ...P746 EN AP G31 Application Notes AP 6 4 MiCOM P746 AP BLANK PAGE...
Page 194: ...P746 EN AP G31 Application Notes AP 6 56 MiCOM P746 AP BLANK PAGE...
Page 196: ...P746 EN PL G31 Programmable Logic MiCOM P746...
Page 238: ...P746 EN MR A11 Measurements and Recording MiCOM P746...
Page 240: ...P746 EN MR A11 Measurements and Recording MR 8 2 MiCOM P746 MR BLANK PAGE...
Page 258: ...P746 EN FD G31 Firmware Design MiCOM P746...
Page 280: ......
Page 348: ...P746 EN MT A11 Maintenance MiCOM P746...
Page 350: ...P746 EN MT A11 Maintenance MT 11 2 MiCOM P746 MT BLANK PAGE...
Page 364: ...P746 EN MT A11 Maintenance MT 11 16 MiCOM P746 MT BLANK PAGE...
Page 366: ...P746 EN TS G31 Troubleshooting MiCOM P746...
Page 368: ...P746 EN TS G31 Troubleshooting TS 12 2 MiCOM P746 TS BLANK PAGE...
Page 382: ...P746 EN SC G31 SCADA Communications MiCOM P746...
Page 424: ...P746 EN SC G31 SCADA Communications SC 13 42 MiCOM P746 SC BLANK PAGE...
Page 426: ...P746 EN SG F21 Symbols and Glossary MiCOM P746...
Page 438: ......
Page 440: ...P746 EN IN G31 Installation IN 15 2 MiCOM P746 IN BLANK PAGE...
Page 468: ......
Page 470: ...P746 EN HI G31 Remote HMI HI 16 2 MiCOM P746 HI BLANK PAGE...
Page 500: ...P746 EN HI G31 Remote HMI HI 16 32 MiCOM P746 HI BLANK PAGE...
Page 502: ......
Page 504: ...P746 EN CS A11G31 Cyber Security CS 17 2 MiCOM P746 CS BLANK PAGE...
Page 524: ...P746 EN VH G31 Firmware and Service Manual Version History MiCOM P746...
Page 529: ......