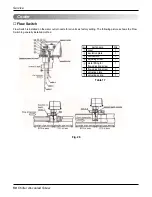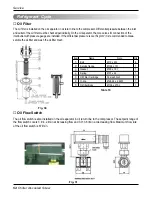
Service
Operation & Maintenance Manual 47
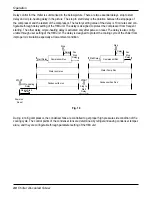
In order to protect the compressor, the compressor has been installed three PTC temperature sensors inside motor
coil and another one at the discharge side of compressor. These sensors are connected to an INT69 control module to
monitor the motor coil temperature and discharge temperature as well. If the temperature in one of the areas moni-
tored exceeds the nominal response temperature of the respective PTC thermistor, the sensor resistance increases
and the INT69 control module switches the motor contactor off. The cutout temperature of the motor winding tempera-
ture is 248°F(120°C) and the cut in temperature is 167°F(75°C). The cutout temperature of the motor winding is
230°F(110°C) and the cut in temperature is 140°F(60°C). Compressor trouble shooting is shown in the above.
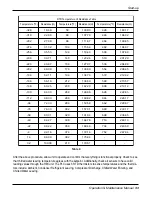
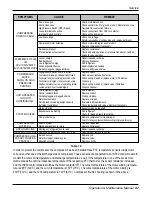
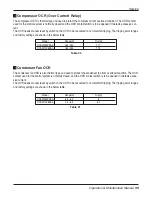
SYMPTOMS
COMPRESSOR
DOES NOT RUN
COMPRESSOR CYCLES
OFF
ON LOW SATURATED
SUCTION TEMPERATURE
COMPRESSOR
SHUTS
DOWN ON HIGH
PRESSURE
CONTROL
UNIT OPERATES
LONG OR
CONTINUOUSLY
SYSTEM NOISES
COMPRESSOR
LOSES OIL
HOT LIQUID LINE
FROSTED LIQUID LINE
COMPRESSOR LOAD-
ERS NOT WORKING
PROPERLY
CAUSE REMEDY
Check main disconnect.
Check control circuit for ground or short. Replace fuse. Use
Navigator to reset current alarms.
Check connections from CCP to contactor.
Check wiring and rewire.
Check line voltage.
Determine location of voltage drop and remedy deficiency.
Check motor winding for open or short.
Replace compressor if necessary.
Replace compressor.
Check oil pump operation, oil pressure transducer, verify oil
solenoid valve operation.
Repair leak and recharge.
Replace transducer.
Add refrigerant.
Repair/replace as needed.
Remove and clean strainer.
Replace switch.
Open valve or replace if defective.
Check wiring. Repair or replace motor(s) if defective.
Clean coil.
Check wiring. Repair or replace valve if defective.
Clean condenser.
Add refrigerant.
Replace control.
Clean or replace.
Replace or repair.
Evaluate load requirements.
Check loader solenoid valves. Replace if necessary.
Support piping as required.
Add refrigerant.
Check for plugged liquid line strainer.
Replace compressor (worn bearings).
Check for loose compressor bolts securing compressor to cooler.
Find and repair leak.
Replace compressor.
Repair leak and recharge.
Open valve or remove restriction.
Replace coil.
Replace valve.
Rewire correctly.
Power line open
Control fuse open
High-Pressure Switch (HPS) tripped
Loose terminal connection
Improperly wired controls
Low line voltage
Compressor motor defective
Seized compressor
Pre-lubrication not successful
Loss of charge
Bad transducer
Low refrigerant charge
Failed expansion device
Partially plugged or plugged strainer
High-pressure switch erratic in action
Compressor discharge valve partially closed
Condenser fan(s) not operating (air cooled units)
Condenser coil plugged or dirty (air cooled units)
Condenser water valve not operating (water
cooled units) Circuit overcharged
Low refrigerant charge
Control contacts fused
Partially plugged or plugged strainer
Defective insulation
Service load exceeding design capacity
Inefficient compressor
Piping vibration
Expansion valve hissing
Compressor noisy
Leak in system
Mechanical damage to rotors
Shortage of refrigerant due to leak
Shutoff valve partially closed or restricted
Burned out coil
Defective loader solenoid valve
Miswired solenoid
Table 16