S1 series standard inverter
-42-
Function
code
Name
Detailed parameter description
Default
value
6: Switch running command reference mode
by sequence
7: Reserved
Tens: Reserved
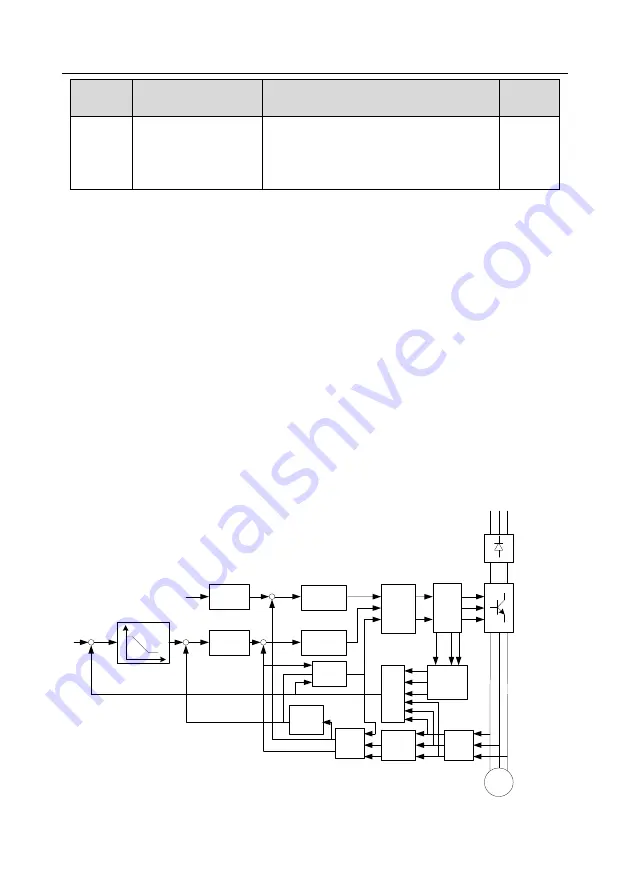
5.5.3 Vector control
Asynchronous motors are featured with high order, non-linear, strong coupling and multi-variables,
which makes it very difficult to control asynchronous motors during actual application. The vector
control theory aims to solve this problem through measuring and controlling the stator current vector
of asynchronous motor, and decomposing the stator current vector into exciting current (current
component which generates internal magnet field) and torque current (current component which
generates torque) based on field orientation principle, and then controlling the amplitude value and
phase position of these two components (namely, control the stator current vector of motor) to realize
decoupling control of exciting current and torque current, thus achieving high-performance speed
regulation of asynchronous motor.
S1 series inverter carries built-in speed sensor-less vector control algorithm. As the core algorithm of
vector control is based on accurate motor parameter model, the accuracy of motor parameters will
impact the control performance of vector control. It is recommended to input accurate motor
parameters and carry out motor parameter autotuning before vector operation.
As vector control algorithm is complicated, users should be cautious of regulation on dedicated
function parameters of vector control.
Calculate i
m
ACR
exciting
current
Flux linkage
observation
Current
detection
Position
observation
Speed
identific
ation
Voltage
detection
ACR
torque current
Calculate i
T
Park
conversion
PWM
pulse
Rectifier
bridge
IGBT
bridge
Motor
Park
conversio
n
Clark
conversion
φ
+
-
+
-
+
-
U
V
U
W
Uu
i
U
i
V
i
W
U
V
U
W
Uu
i
M
i
T
1
w
r
1
w
r
φ
i
T
R S T
















































