5-2
Cisco MGX 8850 Routing Switch Command Reference
Release 2.0, Part Number 78-10467-04 Rev C0, October 2001
Chapter 5
PNNI Commands
PNNI Addressing
PNNI Addressing
The PNNI addresses and identifiers contain fields that are common to each other and should match each
other. If you change a field in one item, Cisco Systems advises you to change the corresponding field in
the other item. For example, if you change the ATM address, you should change corresponding fields in
the PNNI summary address and node identifier. Note that the peer group identifier does not share in this
recommendation.
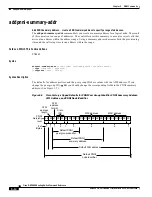
The name and graphic representation of each address and identifier as well as the common information
appears in
Figure 5-1
. The central and lower parts show the breadth of each item. Applicable command
descriptions point out where you should modify common fields. The following fields also go into the
construction of the ATM addresses and PNNI-related identifiers:
•
The Initial Domain Identifier (IDI) identifies the domain.
•
The Initial Domain Part (IDP) identifies the country.
•
The Authority and Format Identifier (AFI) identifies the address format and who provided it.
•
The Data Country Code (DCC) identifies the country.
Figure 5-1
Cisco Factory-shipped Node-Addressing Defaults Mapping into Both NSAP and DCC
Address Formats
47
1
1
1
# of
Bytes
2
1
Default PNNI
peer group identifier
1
3
6
6
00
56 160
91 81 00 00 00 XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX 00
53383
Cisco
ICD
MAC address
DCC
ESI
SEL
AFI
39
MAC address
ATM
address
length
PNNI
hierarchy
level
Default PNNI
summary address
Default ATM address
Default PNNI
node identifier
High order DSP
(10 bytes)
20 byte ATM address
IDI
Host address
(7 bytes)
DSP: Domain Specific Part
DSP: Domain Specific Part
IDP
(3 bytes)
ATM
address
format
ATM
address
format