61
of 148
The [
↑
] and [
↓
] cursor keys are used to select the various coefficients. The selected parameter is displayed
inversely.
The [POS1] key is used to select the 1st parameter in the window.
The [END] key is used to select the last parameter in the window.
The required coefficient can now be entered:
Pressing the [F1] key (INPUT) invokes the input mode.
Numeric keys [0] to [9] , the decimal key [
.
] and the sign key are used to enter the coefficient.
The [BSP] key is used to delete the character entered last.
The [C] key is used to delete all the entered characters and repeat the input procedure from the beginning,
without exiting the input mode.
The [ESC] key is used to cancel the current entry, and exit the input mode.
Pressing the [ENT] key saves the new value if it is valid, and exits the input mode.
Note:
The coefficients entered by the manufacturer comply with DIN EN 60751 for positive temperatures.
The C coefficient cannot be entered (only positive temperatures).
DIN EN 60751 values are always used for negative temperatures (< 100
Ω
).
Scaling the current input
The (linear) current input is scaled in this menu.
Example:
A temperature sensor indicates an output current of 2 mA at 20 °C and 20 mA at 100 °C.
The input current can have a value ranging from 0 ... 20 mA .
[F3] key (HOME):
This effects a return to the main menu.
[F4] key (RETUrn):
This effects a return to the scaling menu.
The [
↑
] and [
↓
] cursor keys are used to select the various parameters. The selected parameter is displayed
inversely.
The [POS1] key is used to select the 1st parameter in the window.
The [END] key is used to select the last parameter in the window.
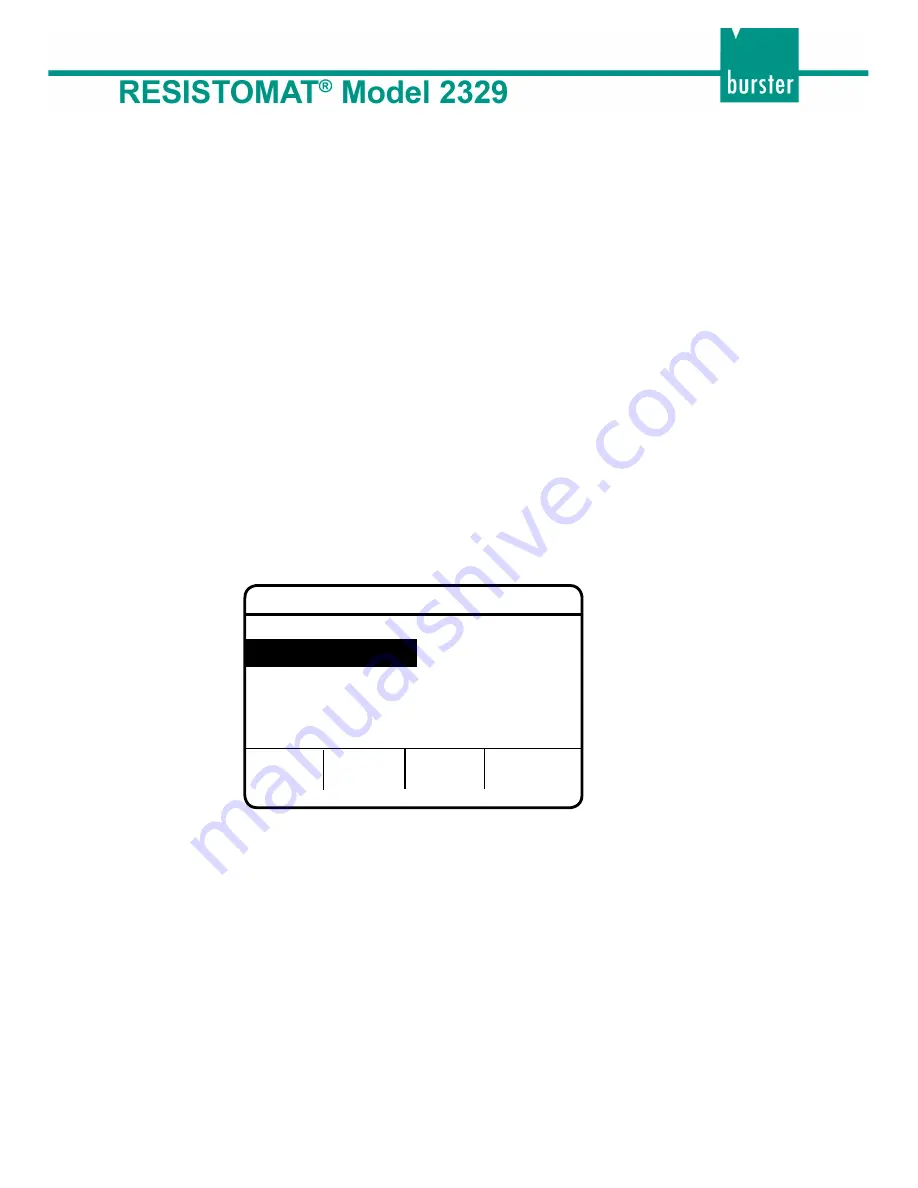
Display of the menu for scaling
the current input
INPUT
HOME RETU
CURRENT INPUT
I1
= 2 mA
t1 = 20 °C
I2 = 20 mA
t2 = 100 °C






























