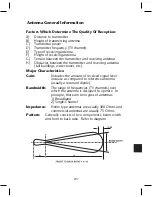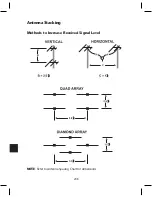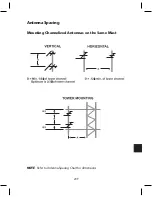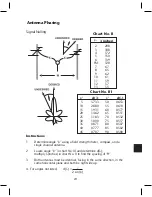
221
Digital Signal Analysis
Interferers are understood to be sinusoidal spurious signals
occurring in the transmission frequency range and superimposed
on the QAM signal at some point in the transmission path. After
demodulation, the interferer is contained in the baseband form of
low-frequency sinusoidal spurious signals. The frequency of these
signals corresponds to the difference between the frequency of
the original sinusoidal interference and the carrier frequency in
the RF band.
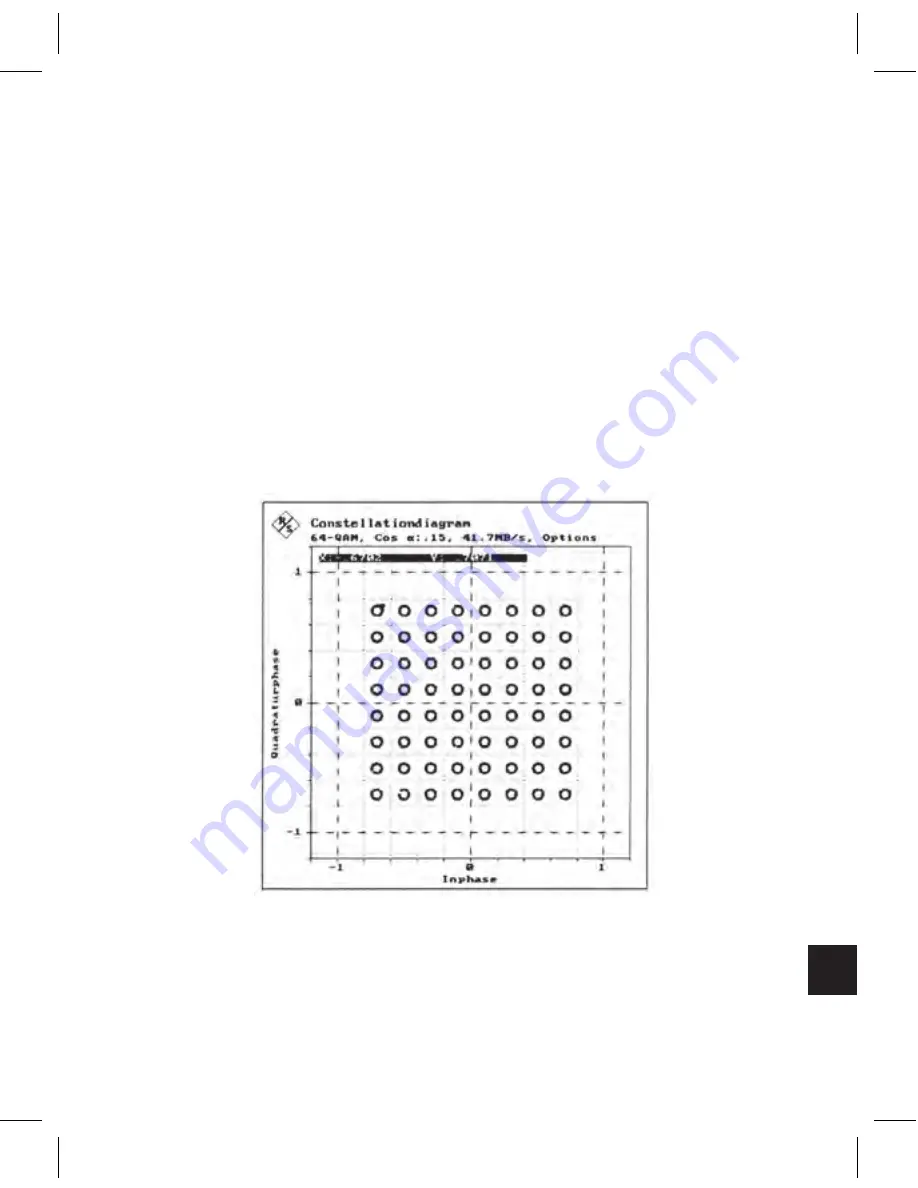
In the constellation diagram, an interferer shows in the form of a
rotating pointer superimposed on each signal status. The example
applies the condition that there is no other error present at the
same time, The constellation diagram shows the path of the
pointer as a circle around each ideal signal status.
Constellation Diagram — 64 QAM signal with
Interferer (C/I = 25.0 dB)
Summary of Contents for AMM-806
Page 86: ...79 TVCB PC Installation ...
Page 93: ...86 SMI Installation Torque Patterns 1 Start Here 2 3 4 5 6 1 Start Here 2 3 4 4 PORT 8 PORT ...
Page 125: ...118 Fiber Optics Fiber Loss vs Path Length Single Mode 1550 nm ...
Page 156: ...149 Cable TV Channel Format NTSC NTSC Composite Video Waveform ...
Page 157: ...150 US Frequency Spectrum ...
Page 158: ...151 FCC Aeronautical Band Frequencies Used for Communication and Navigation ...
Page 175: ...168 Common CATV Symbols ...
Page 176: ...169 Common CATV Symbols ...
Page 177: ...170 Digital L Band Distribution Symbols ...
Page 178: ...171 Digital L Band Distribution Symbols ...
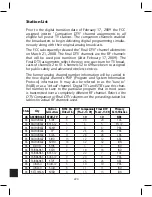
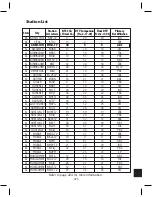
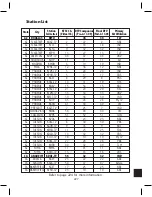
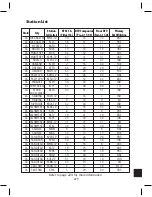
Page 183: ...176 Typical Cable Attenuation Chart in dB 100 Feet 68 F 20 C ...
Page 187: ...180 Echo Rating Graph ...
Page 188: ...181 Signal to Interference Limits Non Coherent Carriers ...
Page 190: ...183 Heterodyne Modulator Analog ...
Page 191: ...184 Heterodyne Processor Analog ...
Page 213: ...206 Multiplexers ...
Page 285: ...Rev 8 0 ...