104
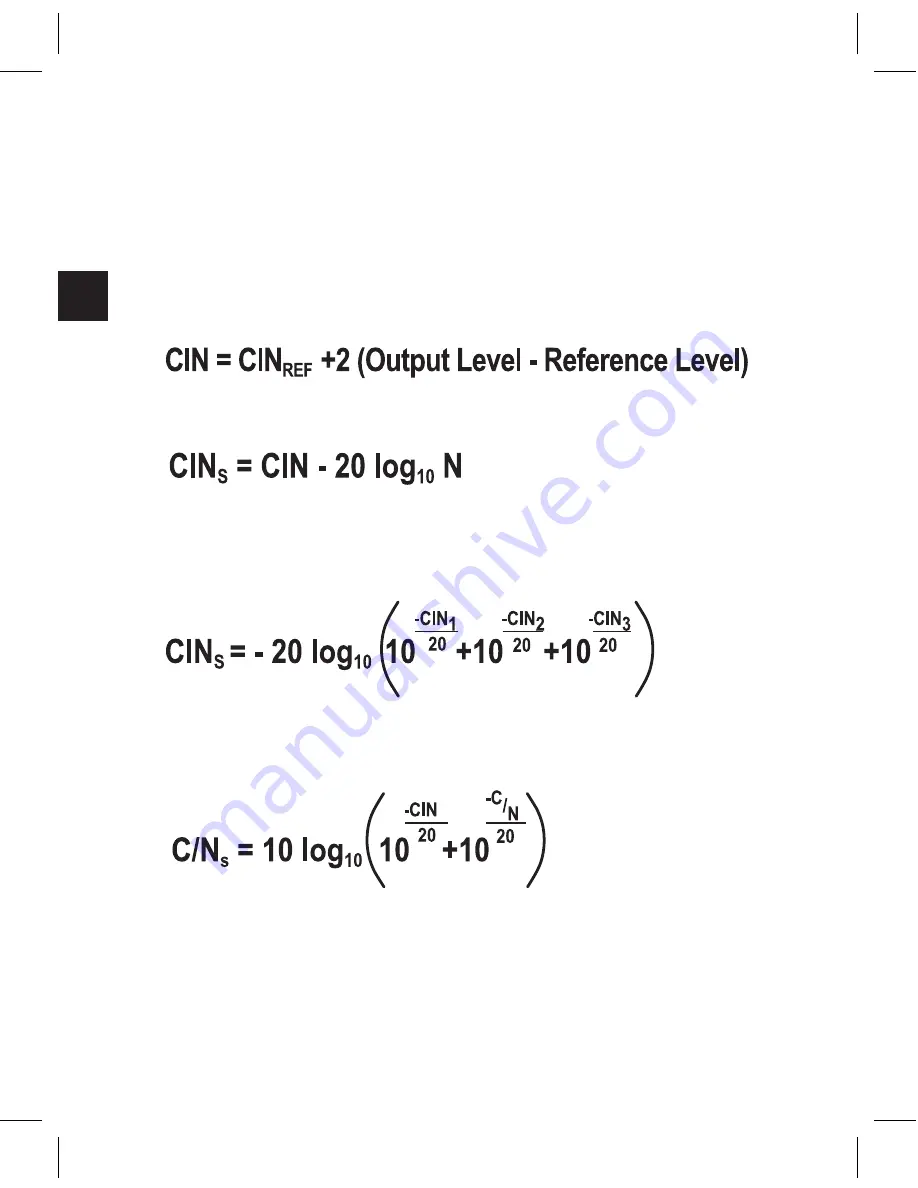
It is assumed that CIN is dominated by 3rd order distortion (CIN3).
This is the case in systems with analog television channels to 550
MHz and digital video above 550 MHz.
1. Composite Intermodulation Noise for One Amplifier at Operating
Level.
2. To Sum Identical Composite Intermodulation Noise Ratios:
See charts & examples starting on pages 84.
3. To Sum Different Composite Intermodulation Noise Ratios:
See examples starting on pages 84.
4. To Sum Carrier/Noise and Composite Intermodulation Ratios:
Rule: CIN behaves like CTB in a cascade of amplifiers, but it adds to the
C/N noise.
Composite Intermodulation Noise (CIN)
System Calculations
Summary of Contents for AMM-806
Page 86: ...79 TVCB PC Installation ...
Page 93: ...86 SMI Installation Torque Patterns 1 Start Here 2 3 4 5 6 1 Start Here 2 3 4 4 PORT 8 PORT ...
Page 125: ...118 Fiber Optics Fiber Loss vs Path Length Single Mode 1550 nm ...
Page 156: ...149 Cable TV Channel Format NTSC NTSC Composite Video Waveform ...
Page 157: ...150 US Frequency Spectrum ...
Page 158: ...151 FCC Aeronautical Band Frequencies Used for Communication and Navigation ...
Page 175: ...168 Common CATV Symbols ...
Page 176: ...169 Common CATV Symbols ...
Page 177: ...170 Digital L Band Distribution Symbols ...
Page 178: ...171 Digital L Band Distribution Symbols ...
Page 183: ...176 Typical Cable Attenuation Chart in dB 100 Feet 68 F 20 C ...
Page 187: ...180 Echo Rating Graph ...
Page 188: ...181 Signal to Interference Limits Non Coherent Carriers ...
Page 190: ...183 Heterodyne Modulator Analog ...
Page 191: ...184 Heterodyne Processor Analog ...
Page 213: ...206 Multiplexers ...
Page 285: ...Rev 8 0 ...