3.3 Resistance Measurements (2 & 4-wire)
The ranges for resistance measurement are 100 Ω, 1KΩ, 10kΩ,
100kΩ, 1MΩ, 10MΩ, and 100MΩ, with a sensitivity of 100 μΩ (on 100
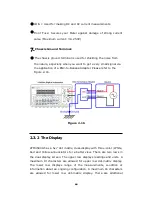
Ω range.) There are two modes for measuring the resistance: 2-wire
mode as shown in
Figure 3-6
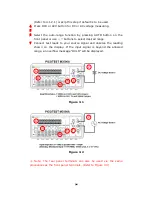
and 4-wire mode as shown in
Figure 3-
7
. With 4-wire mode, the test current is measured from the test
resistance through one pair of the test leads, and the test voltage
across the resistance under test is measured from another set of the
test leads. As a result, the 4-wire mode is more accurate for low
resistance measurements. The trade off is the longer settling time for
4-wire mode.
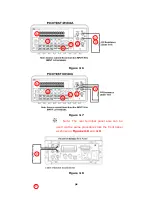
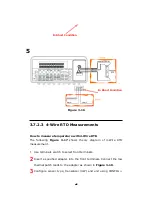
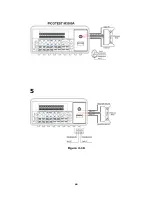
Figure 3-8
and
3-9
show the input terminal connections on the rear
panel for 2-wire mode and 4-wire mode respectively.
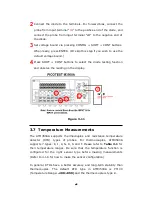
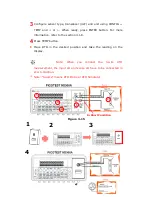
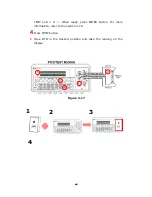
How to measure resistance
1
Selects input signal connections on front or rear panel.
2
Connect the test leads to the terminals as shown in
Figure 3-6
(2-
wire) or
Figure 3-7
(4-wire).
3
Set RESOLUTION (Refer to 4.1.3) or skip this step if default is to be
used.
4
Press Ω2 button for 2-wire measurement or SHIFT + Ω2 buttons for
4-wire measurement.
5
Select the auto-range function by pressing AUTO button on the
front panel or use
△
and
▽
buttons to select the desired range.
6
Connect test leads to your source signal and observe the reading
shown on the display. If the input signal is greater than the allowed
range, an overflow message “OVLD” will be displayed.
37