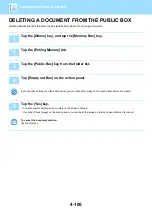
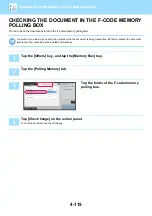
4-107
PERFORMING F-CODE COMMUNICATION
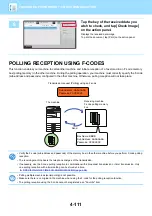
How F-codes work
A fax that is transmitted with an F-code is received in the memory box of F-code communication in the receiving
machine specified by the F-code (sub-address and passcode). If the F-code sent by the transmitting machine does not
match the F-code in the receiving machine, reception will not take place.
The products of other manufacturers may use different terms for "Sub Address" and "Passcode". If you need to contact
the operator of another machine regarding sub-addresses and passcodes, refer to the terms used by the ITU-T in the
table below.
CREATING MEMORY BOXES IN THE MACHINE FOR
F-CODE COMMUNICATION
Before the F-code communication function can be used, special memory boxes must be created in "Settings".
Set the box name and F-code (sub-address and passcode) in each memory box, and store them.
After you have created a memory box, notify the other party of F-code communication of the sub-address and passcode
of the box.
To use the following F-code communication functions, F-code memory boxes must be created in your machine.
• F-code confidential reception
• F-code polling memory
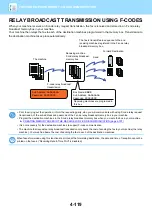
• F-code relay broadcast transmission
To use the following F-code communication functions, F-code memory boxes must be created in the other machine.
• F-CODE CONFIDENTIAL TRANSMISSION
• F-code polling reception
• F-code relay request transmission
The machine
ITU-T
F-code polling memory box
F-code confidential box
F-code relay broadcasting function
Sub Address
SEP
SUB
SUB
Passcode
PWD
SID
SID
An F-code consists of a sub-address and passcode, and cannot be longer than 20 digits.
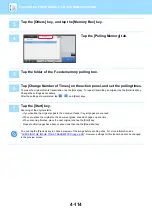
To create F-code memory boxes:
Create in "Settings" - [System Settings]
→
[Image Send Settings]
→
[Fax Settings]
→
[F-Code Memory Box].
Memory Box
• Memory Box Name
• Sub Address
• Passcode
• Recipient (only for F-code relay
broadcast transmission)
• Print PIN
(only for F-code confidential
reception)