Platform Management ArchitectureIntel® Server Board SE7520BD2 Technical Product Specification
72
Revision
1.3
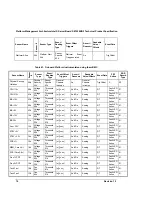
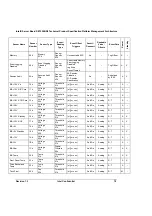
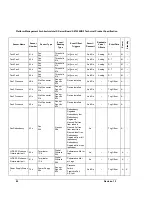
controller. Sensor Data Records provide a list of the sensors, their characteristics, location,
type, and associated Sensor Number, for sensors in a particular system. The Sensor Data
Records also hold default threshold values (if the sensor has threshold based events), factors
for converting a sensor reading into the appropriate units (mV, rpm, degrees Celsius, etc.), and
information on the types of events that a sensor can generate.
Sensor Data Records also provide information on where Field Replaceable Unit (FRU)
information is located, and information to link sensors with the entity and/or FRU they’re
associated with.
Information in the SDRs is also used for configuring and restoring sensor thresholds and event
generation whenever the system powers up or is reset. This is accomplished via a process
called the ‘initialization agent’. The BMC reads the SDRs and based on bit settings, writes the
threshold data. Then it enables event generation for the various sensors it monitors and in
management controllers on the IPMB for systems based on the Standard or Advanced
management models.
System Management Software uses the data contained in the Sensor Data Record information
to locate sensors in order to poll them, interpret, and present their data readings, adjust
thresholds, interpret SEL entries, and alter event generation settings.
In Standard and Advanced management models, SDRs also provide a mechanism for
extending the baseboard management with additional chassis or OEM ‘value-added’ monitoring
and events. The baseboard monitoring can be extended by implementing an IPMI-compatible
management controller, connecting it to the IPMB, and adding new SDRs describing that
controller and its sensors to the SDR Repository. System Management Software can then read
the SDRs and use them to automatically incorporate the additional sensors.
4.1.5 Private
Management
Buses
A ‘Private Management Bus’ is a single-master I
2
C bus that is controlled by the management
controller. Access to any of the devices on the Private Management Bus is accomplished
indirectly via commands to the management controller via the IPMB or system interfaces.
Private Management buses are a common mechanism used for accessing temperature
sensors, system processor information, and other baseboard monitoring devices that are
located in various locations in the system.
The devices on the Private Management Bus are isolated from traffic on the IPMB. Because
devices (such as temperature sensors) are polled by the management controller, this removes
the polling traffic from the ‘public’ IPMB bus. This also increases the reliability of access to the
information, since issues with IPMB bus arbitration and message retries are avoided.
Furthermore, placing managed I
2
C devices on the private management bus frees up the I
2
C
addresses that those devices would have used up on the IPMB.
4.1.6 Management
Controllers
At the heart of platform management is a management controller. To support the tiered
management model, the Server Board SE7520BD2 supports two different management
controllers. Integrated onto the baseboard is the National Semiconductor* Mini-BMC (mBMC) to
provide the functionality of the Essentials management tier. The Standard and Advanced
modules electrically replace the Mini-BMC with the more full featured ‘Sahalee’ microcontroller.